Deciding to learn a new language is a big step. Choosing between Spanish and Portuguese can be tough. These two languages are close relatives, both coming from Latin. They share some similarities but also have their own unique features. This guide will help you see which language suits you better by looking at their sounds, grammar, and words. We’ll also talk about how easy they are to learn and their uses in everyday life.

Key Takeaways
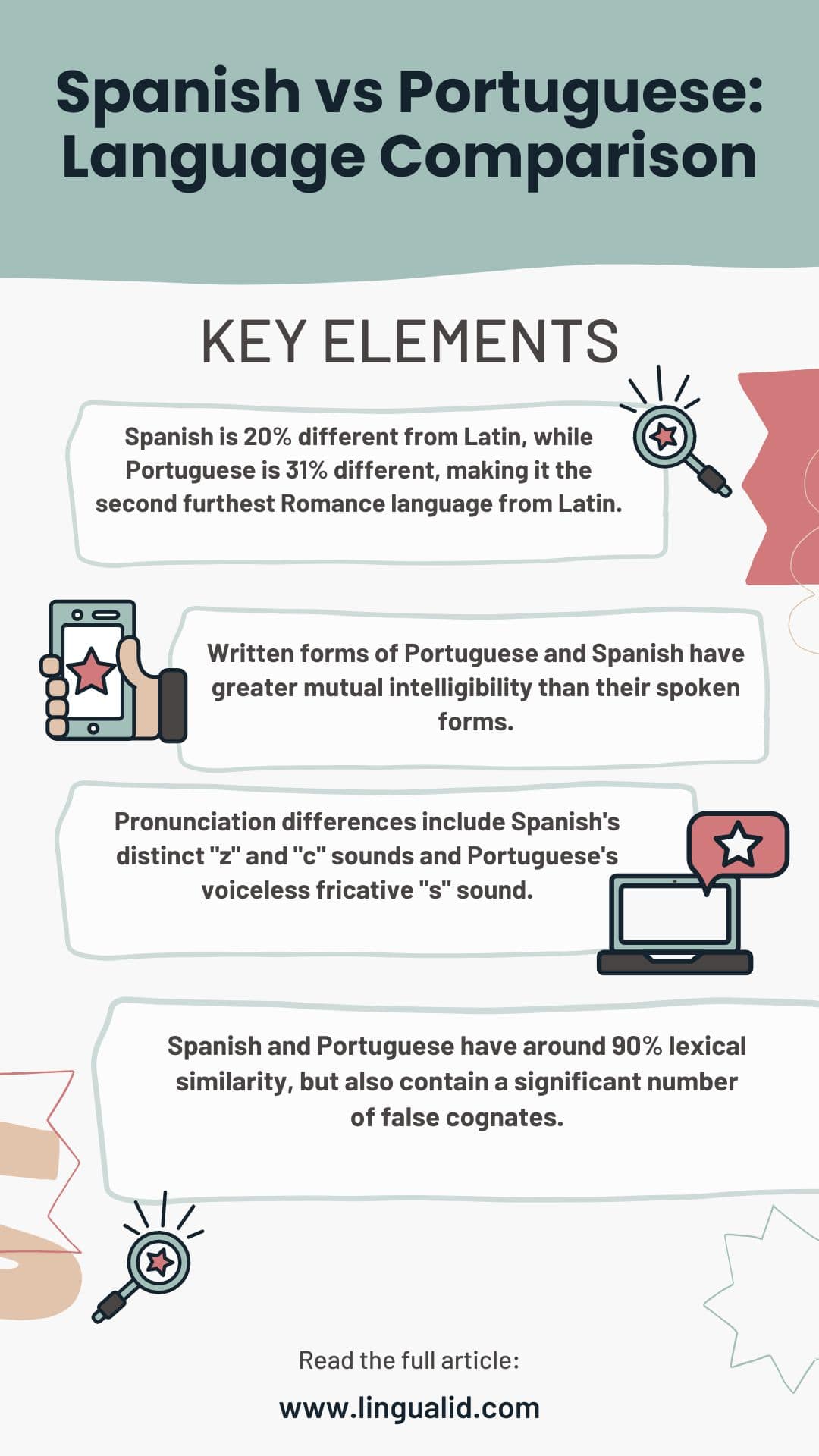
- Spanish is 20% different from Latin, while Portuguese is 31% different, making it the second furthest Romance language from Latin.
- Written forms of Portuguese and Spanish have greater mutual intelligibility than their spoken forms.
- Pronunciation differences include Spanish’s distinct “z” and “c” sounds and Portuguese’s voiceless fricative “s” sound.
- Spanish and Portuguese have around 90% lexical similarity, but also contain a significant number of false cognates.
- Spanish and Portuguese have distinct word order, with Spanish following a Subject-Verb-Object pattern and Portuguese a Subject-Object-Verb pattern.
- Key Takeaways
- Overview of Spanish and Portuguese Languages
- Importance of Choosing the Right Language to Learn
- Shared Latin Alphabet
- Similar Conjugation Rules
- Null-Subject Languages
- Phonology and Pronunciation Distinctions
- Grammatical Contrasts
- Historical Divergence
- Classification by U.S. Foreign Service Institute
- Immersive Learning Techniques
- Global Presence and Business Opportunities
- Travel and Cultural Enrichment
- Cognitive Advantages
- Cultural Understanding
- Multilingual Potential
- Spanish Dialects
- Portuguese Dialects
- Immersive Learning Methods
- Time Commitment Considerations
- What are the key similarities between Spanish and Portuguese?
- How do the phonology and pronunciation differ between Spanish and Portuguese?
- Which language is considered easier to learn for native English speakers?
- What are the global presence and business opportunities for each language?
- What are the cognitive benefits of learning a new language?
- How do the dialects of Spanish and Portuguese differ?
- What are the similarities and differences in vocabulary between Spanish and Portuguese?
- What are some effective learning methods for Spanish and Portuguese?
Introduction
Spanish and Portuguese are the top languages in Central and South America. They have a long history, from the Iberian peninsula. These romance languages are similar but also have their own unique features. Knowing these differences is key when deciding which language to learn.
Overview of Spanish and Portuguese Languages
Spanish and Portuguese come from Latin, which spread across Europe during the Roman Empire. They have changed over time but kept many similarities in words, grammar, and how they sound.
Importance of Choosing the Right Language to Learn
Learning Spanish or Portuguese can open new career doors, let you dive into a new culture, or challenge your brain. By understanding the similarities and differences, you can pick the language that fits your goals best.
Similarities Between Spanish and Portuguese
Spanish and Portuguese may seem different at first glance, but they share many similarities. These similarities make learning one language easier if you know the other.
Shared Latin Alphabet
Both languages use the same Latin alphabet, except for the Spanish “ñ” and the Portuguese “nh”. This common base in the Roman script helps with understanding and recognition between the two languages.
Similar Conjugation Rules
The way verbs are changed in Spanish and Portuguese is similar. Regular verbs follow the same patterns. This makes learning verb forms in one language easier if you know the other.
Null-Subject Languages
Spanish and Portuguese don’t always need subject pronouns because the verb tells us who is doing the action. This makes speaking and writing in both languages simpler.
About 50% to 60% of what is said in Portuguese can be understood by Spanish speakers, and vice versa. This shows how similar their grammar and words are. This similarity can make learning either language easier.
Key Differences Between Spanish and Portuguese
Spanish and Portuguese come from the same Latin roots but have grown apart over time. They have different sounds, rules, and histories. Knowing these differences is key for those learning one or both languages.
Phonology and Pronunciation Distinctions
Portuguese has a richer sound with more vowel types than Spanish. The way Portuguese sounds change around other letters and in different areas is complex. This is especially true when comparing European and Brazilian Portuguese.
Grammatical Contrasts
Spanish and Portuguese have different grammar, such as how verbs change and how nouns have different genders. Portuguese has more verb tenses and pronouns than Spanish. These differences can make switching between the languages hard.
Historical Divergence
Spanish and Portuguese grew from Vulgar Latin but took different paths over time. They were shaped by their cultures and places. This led to unique words, sayings, and structures that make them distinct.
| Characteristic | Spanish | Portuguese |
|---|---|---|
| Vowel System | 5 Vowels | 14 Vowels |
| Pronunciation Complexity | Relatively Simple | More Complex |
| Verb Tenses | 14 Tenses | 16 Tenses |
| Pronouns | 6 Personal Pronouns | 9 Personal Pronouns |
| Native Speakers | 500 Million | 260 Million |
Ease of Learning: Spanish vs Portuguese
Learning Spanish or Portuguese can be easy for English speakers. The U.S. Foreign Service Institute says both languages are “Category I”. This means they are among the easiest to learn.
Classification by U.S. Foreign Service Institute
The U.S. Foreign Service Institute (FSI) rates languages by how long it takes for English speakers to get good at them. Spanish and Portuguese are both “Category I” languages. They are the easiest to learn and need about 24-30 weeks of hard study to get to a professional level.
Immersive Learning Techniques
Learning Spanish or Portuguese has big benefits. They both use a Latin alphabet and have similar grammar and lots of shared words. This makes switching between the two easier. Using language immersion, listening to podcasts, and watching shows in the target language helps a lot.
Portuguese is spoken by 200-210 million people around the world. It’s spoken on five continents. This gives learners lots of chances to practice and get into the culture, making learning more fun.
Usefulness and Career Prospects
Spanish and Portuguese are both great for your career and daily life. Spanish is the second most spoken language, with over 480 million native speakers in 44 countries. It opens doors to a huge global market.
Many employers, especially in areas with lots of Spanish speakers, look for people who speak both Spanish and their native language. This can help you connect better with clients and workmates.
Global Presence and Business Opportunities
Portuguese isn’t as widely spoken as Spanish, but it’s still very valuable. It’s the sixth most spoken language, with over 265 million speakers in Portugal, Brazil, Angola, and Mozambique.
The growth of online shopping and strong industries in these countries make Portuguese a great skill for your career. It can help you grow professionally.
Travel and Cultural Enrichment
Both Spanish and Portuguese offer amazing cultural experiences for travelers. They share a common Latin heritage, making them easier to learn and understand. This makes traveling in these countries more enjoyable.
You can connect with locals, dive into the culture, and really feel the spirit of the Iberian and Latin American regions.
Choosing to learn Spanish or Portuguese can open up new career paths and cultural experiences. It’s a great way to expand your language skills and discover new worlds.
Benefits of Learning a New Language
Learning a new language opens up many doors. It boosts your brain, helps you understand different cultures, and can make you more attractive to employers. By studying a new language, you can improve your thinking skills and get a deeper look into other cultures.
Cognitive Advantages
Being bilingual can make you sharper. It helps with memory, focus, making decisions, and being creative. Learning new languages also keeps your brain healthy as you age, lowering the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Getting better at a second language also makes your first language stronger. This boosts your overall language skills.
Cultural Understanding
Knowing a new language lets you connect deeply with different cultures and traditions. It gives you a richer understanding of people, their values, and their lives. This helps you be more empathetic and open-minded.
It makes you better at communicating with people from around the world. You can connect with them on a deeper level.
Multilingual Potential
In today’s global world, speaking multiple languages is a big plus. Employers look for people who can speak more than one language. This can lead to better job opportunities and faster career growth.
Learning languages also makes you better at solving problems and handling tasks at once. This makes multilingual people very valuable in the workplace.
Dialects and Regional Variations
The Spanish and Portuguese languages show a lot of regional dialect diversity. These languages have changed over centuries, influenced by history and geography. This has led to different linguistic variations around the world.
Spanish Dialects
Castilian Spanish is the most spoken dialect, from the Iberian Peninsula. But, there are other regional variations too. For example, Andalusian Spanish, from southern Spain, often drops “s” sounds at the end of words.
Spanish in Mexico, the Caribbean, and Latin America also has its own features. These reflect the rich culture of these areas.
Portuguese Dialects
Portuguese has many regional dialects too. In Portugal, there are four main dialects: northern, southern, Azorean, and Madeiranese. In Brazil, there are sixteen distinct dialects, like Caipira, North Coast, and Baiano.
These differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar make Portuguese rich and diverse.
Exploring Spanish and Portuguese dialects is rewarding for language learners and fans. It deepens cultural understanding and improves communication. It also shows the rich linguistic heritage of these Romance languages.
Vocabulary Similarities and False Cognates
Spanish and Portuguese share a lot of words because they both come from Latin. Many words look the same but might sound different. This can be helpful and tricky for those learning these languages.
Statistics show that Spanish and Portuguese share similarities in certain words. For example, roxo in Portuguese means “purple,” but rojo in Spanish means “red.” This shows how words can change over time but keep their roots.
But, there are also false cognates that can confuse learners. For instance, English embarrassed and Spanish embarazada are not the same. Embarazada actually means “pregnant.”
False cognates can also happen between languages far apart, like English and Russian. For example, sympathetic in English and симпатичный (simpatichnyj) in Russian mean different things. This shows how words can sound the same but have different meanings.
Words can change meanings over time, leading to false cognates. For example, the English word silly used to mean “happy.” Now, it means “ridiculous.” The German word selig used to mean “happy” too, but now it means “blessed” or “fortunate.”
These examples show how languages change and how false cognates can happen. They come from changes in how words sound and what they mean over time.
| Language Pair | Percentage of False Cognates |
|---|---|
| Romance Languages (French, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian) | 40% |
| English and French | 15% |
| Dutch and English | 20% |
| Spanish and English | 10% |
| Germanic Languages (German, English, Dutch) | 30% |
Learning Approaches and Strategies
Learning Spanish or Portuguese can be different for everyone. The way you learn affects your progress. Let’s look at two important factors – immersive learning and how much time you spend learning.
Immersive Learning Methods
Methods like the Berlitz Method focus on talking and fully immersing in the language. Watching movies, listening to music, and talking every day can make you fluent faster. These methods are great for learning how to communicate in real situations, not just grammar and words.
Time Commitment Considerations
How much time you spend learning affects your progress. Spanish is easier for English speakers, needing about 480 hours to get good at it. Portuguese might take a bit longer, around 600 hours. But, this can change based on your learning style and how much you immerse yourself in the language.
Using immersive learning and sticking with it can really help you get fluent in Spanish or Portuguese. Knowing the special things about each language lets you learn better and reach your goals.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into the Spanish and Portuguese languages and found many similarities and differences. They both come from Latin, which shows in their words, grammar, and structure. But, they also have their own unique sounds and grammar rules.
These languages have a shared history but have also changed over time in different places. This makes each language its own. As we learn about them, we see how they connect and differ.
Learning Spanish or Portuguese can be rewarding for many reasons. It can make you smarter, help you understand different cultures, and open up new job chances. The choice between the two depends on what you like, what you want to do, and what culture you connect with.
Whether you like the sound of Portuguese or Spanish, this guide has given you a good start in learning. With hard work, using real-life ways to learn, and enjoying the details of each language, you can open up a new world. You’ll gain better ways to communicate, understand others, and grow personally.
FAQ
What are the key similarities between Spanish and Portuguese?
Spanish and Portuguese share a common Latin-based alphabet and similar verb rules. They are both null-subject languages, meaning they often drop subject pronouns.
How do the phonology and pronunciation differ between Spanish and Portuguese?
Portuguese has more vowel sounds than Spanish, making its phonology richer. The pronunciation in Portuguese is complex, changing with the letters around it and by region.
Which language is considered easier to learn for native English speakers?
The U.S. Foreign Service Institute says Spanish is easier for English speakers to learn. Portuguese is seen as harder.
What are the global presence and business opportunities for each language?
Spanish is the second most spoken language, with over 480 million native speakers. Portuguese is official in several countries, including Brazil, and is growing fast in Europe. Many employers look for bilingual skills, especially in areas with many Spanish or Portuguese speakers.
What are the cognitive benefits of learning a new language?
Being bilingual boosts memory, focus, decision-making, and creativity. Learning languages also helps prevent cognitive decline, including Alzheimer’s disease.
How do the dialects of Spanish and Portuguese differ?
Castilian Spanish is the most common dialect. Andalusian Spanish, from southern Spain, often drops the “s” sound at the end of words. Other dialects exist in Mexico, the Caribbean, and Latin America. European and Brazilian Portuguese also have different pronunciation patterns.
What are the similarities and differences in vocabulary between Spanish and Portuguese?
Spanish and Portuguese have many similar words due to their Latin roots. Many words look the same but sound different. This can help and hinder language learners.
What are some effective learning methods for Spanish and Portuguese?
Immersive methods like the Berlitz Method focus on speaking and full language immersion. Watching films, listening to music, and daily conversations can also improve fluency naturally.
Oualid Cheddadi is the founder of Lingualid, a platform that inspires independent language learners worldwide, regardless of the language they are learning. The name “Lingualid” is derived from the Portuguese word for “language,” “língua,” and the last three letters of Oualid’s name, “Lid.”