The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) has made a detailed ranking. It shows how long English speakers need to learn a language to get to “Speaking 3: General Professional Proficiency in Speaking (S3)” and “Reading 3: General Professional Proficiency in Reading (R3)”. This ranking gives a clear view of how hard it is to learn different languages. It’s based on the FSI’s vast experience teaching languages to thousands of students over about 76 years.
Learning a language can be different for everyone, but the FSI‘s ranking helps show how hard it might be. They look at things like how similar the language is to English, its grammar, and how hard the pronunciation is. This helps them make a detailed ranking of language difficulty for English speakers starting to learn a new language.
Key Takeaways
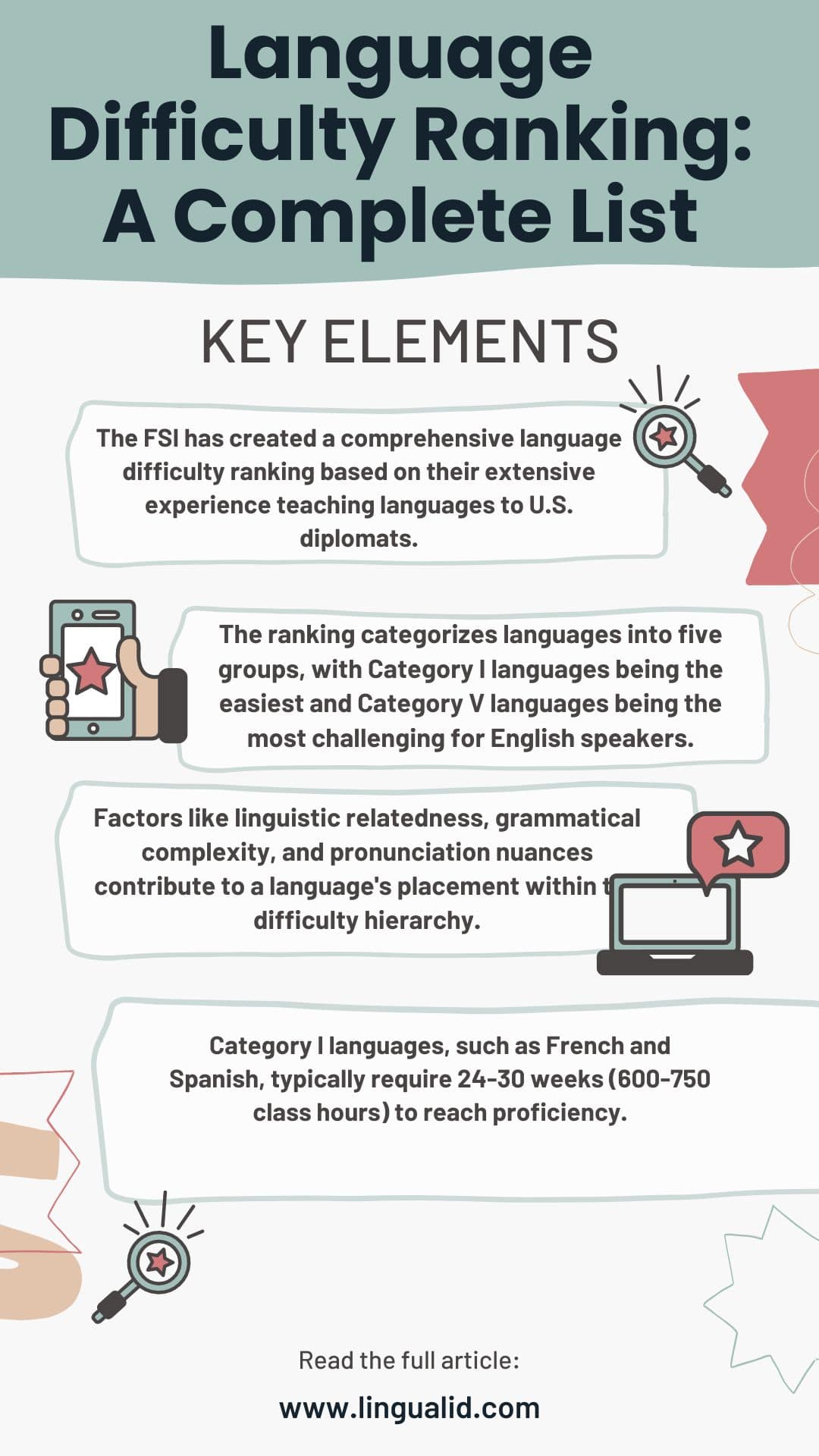
- The FSI has created a comprehensive language difficulty ranking based on their extensive experience teaching languages to U.S. diplomats.
- The ranking categorizes languages into five groups, with Category I languages being the easiest and Category V languages being the most challenging for English speakers.
- Factors like linguistic relatedness, grammatical complexity, and pronunciation nuances contribute to a language’s placement within the difficulty hierarchy.
- Category I languages, such as French and Spanish, typically require 24-30 weeks (600-750 class hours) to reach proficiency.
- Category V languages, including Mandarin Chinese, Cantonese, Japanese, Korean, and Arabic, demand around 88 weeks (2200 class hours) for proficiency.
- Key Takeaways
- What Factors Influence Language Difficulty for English Speakers?
- Overview of the FSI Language Difficulty Categories
- Category I: Closely Related Languages (23-24 Weeks)
- Category II: German (30 Weeks)
- Category III: Cultural and Linguistic Differences (36 Weeks)
- Category IV: Significant Differences from English (44 Weeks)
- Category V: Exceptionally Challenging Languages (88 Weeks)
- What is the Foreign Service Institute (FSI) language difficulty ranking?
- What factors influence language difficulty for English speakers?
- What are the FSI language difficulty categories?
- Why are the "super-hard languages" so difficult for English speakers to learn?
- Is the FSI language difficulty ranking definitive?
Introduction to Language Difficulty Rankings
There’s no clear answer to which languages are easiest or hardest. Yet, the Foreign Service Institute (FSI) offers a helpful framework. It ranks languages by how long it takes English speakers to become proficient. This means reaching a level of “Professional Working Proficiency,” which is like scoring “Speaking-3/Reading-3” (S-3/R-3) on a certain scale.
What Factors Influence Language Difficulty for English Speakers?
Several factors affect how hard a language is for English speakers. Grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and writing systems play big roles. Languages that are farthest from English in these areas are usually harder to learn.
Overview of the FSI Language Difficulty Categories
- Category I: Closely related languages, requiring 23-30 weeks (600-750 class hours) to reach proficiency.
- Category II: Languages with some linguistic and/or cultural differences, requiring about 36 weeks (900 class hours).
- Category III: Languages with significant linguistic and/or cultural differences, requiring approximately 44 weeks (1,100 class hours).
- Category IV: “Super-hard” languages, requiring 88 weeks (2,200 class hours).
We’ll look at which languages fall into each category in the next sections.
language difficulty ranking: Breaking Down the Categories
The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) has sorted languages into five groups. These groups show how long it takes English speakers to get good at a language. Let’s look at the first two groups.
Category I: Closely Related Languages (23-24 Weeks)
Category I languages are the easiest for English speakers to learn. They need about 23-24 weeks or 575-600 class hours to get proficient. This group includes languages like Afrikaans, Danish, Dutch, French, Italian, Norwegian, Portuguese, Romanian, Spanish, and Swedish.
These languages are similar to English in grammar, words, and how they sound. This makes learning them easier for English speakers.
Related: Easiest Languages To Learn For English Speakers
Category II: German (30 Weeks)
Category II includes German, which is a bit harder. German has complex grammar, like cases and word order. English speakers need about 30 weeks or 750 class hours to get good at German.
| Language Category | Estimated Weeks | Estimated Class Hours | Example Languages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category I | 23-24 weeks | 575-600 hours | Afrikaans, Danish, Dutch, French, Italian, Norwegian, Portuguese, Romanian, Spanish, Swedish |
| Category II | 30 weeks | 750 hours | German |
As we move up the language difficulty scale, things get harder. English speakers face more challenges. We’ll look at the harder categories next.
The Challenges of More Distant Languages
When we dive into learning new languages, some are harder for English speakers. These languages, in Categories III and IV, need a lot more time and effort. They have big cultural and linguistic differences from English.
Category III: Cultural and Linguistic Differences (36 Weeks)
Languages like Indonesian, Malaysian, and Swahili are tough for English speakers. They have complex grammar, new words, and writing systems not like English’s. Getting used to these differences takes time and requires diving deep into the language and culture.
Category IV: Significant Differences from English (44 Weeks)
Languages in Category IV, such as Albanian, Amharic, Armenian, Azerbaijani, and Bengali, are even harder. They have very different grammar, writing, and sounds from English. For example, Arabic has a unique alphabet and script that’s hard for English speakers. Mandarin Chinese is tough because of its tones and idioms. Japanese has three writing systems with thousands of characters, making it complex.
Learning these languages means being dedicated, patient, and open to the culture. With hard work and a real interest, English speakers can overcome these challenges. They can discover the beauty of these languages.
Related: Try our Language Learning Duration Estimator.
The Super-Difficult Languages for English Speakers
Some languages are tough for native English speakers, but a few are super hard. These “super-hard languages” have grammar, vocabulary, and writing systems very different from English. This makes them tough for English learners.
Category V: Exceptionally Challenging Languages (88 Weeks)
The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) calls some languages “exceptionally challenging” for English speakers. Arabic, Cantonese, Mandarin Chinese, Japanese, and Korean are in this group. They need an average of 88 weeks or 2,200 hours of hard study to get good at them.
- Mandarin Chinese is the most spoken native language, with 918 million speakers. Its writing system and four tones are hard for English speakers.
- Arabic is in the top five most-spoken languages. It has many dialects, a right-to-left script, and complex grammar, making it hard for English speakers.
- Japanese and Korean languages also belong here. They have unique writing systems and complex grammar unlike English.
Learning these “exceptionally challenging languages” takes a lot of hard work and effort from English speakers. But, it can be very rewarding, both personally and professionally.
Conclusion
The FSI language difficulty ranking helps English speakers see how hard different languages are to learn. It looks at grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and writing systems. This gives us clues on what makes a language tough or easy.
Even the toughest languages can be learned with hard work, good strategies, and regular practice. It’s important to keep an open mind and be ready to learn about the language’s culture and unique traits.
Knowing about language difficulty rankings helps English speakers plan their learning better. They can set achievable goals, use their time and resources wisely, and find the best ways to study. This way, they can reach the language level they want.
FAQ
What is the Foreign Service Institute (FSI) language difficulty ranking?
The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) lists languages by how long English speakers need to learn them. They aim for “Speaking 3: General Professional Proficiency in Speaking (S3)” and “Reading 3: General Professional Proficiency in Reading (R3)”. This ranking might not match everyone’s experience, but it’s based on the FSI’s vast teaching experience over 70 years.
What factors influence language difficulty for English speakers?
Grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and writing systems affect how hard a language is for English speakers.
What are the FSI language difficulty categories?
The FSI divides languages into categories based on difficulty. Category I includes languages like Afrikaans and French, which are easier for English speakers. Category II has German, known for its complex grammar. Category III includes languages like Indonesian, which are quite different from English.
Category IV covers languages like Albanian, which are even more challenging. Category V, the hardest, includes languages like Arabic and Mandarin, which are very tough for English speakers.
Why are the “super-hard languages” so difficult for English speakers to learn?
Languages in Category V, like Arabic and Mandarin, are very hard for English speakers. They have unique grammar, vocabulary, and writing systems that differ a lot from English.
Is the FSI language difficulty ranking definitive?
The FSI ranking gives a general idea of how hard languages are for English speakers. But, it’s not set in stone. People learn at different paces, and some might find certain languages easier or harder than the ranking suggests.
Oualid Cheddadi is the founder of Lingualid, a platform that inspires independent language learners worldwide, regardless of the language they are learning. The name “Lingualid” is derived from the Portuguese word for “language,” “língua,” and the last three letters of Oualid’s name, “Lid.”