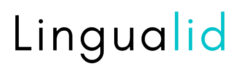Learning common verbs in German opens the door to better communication. It doesn’t matter if you’re just starting or have some experience. Knowing verbs like “haben” and “sein” is key to sharing complex ideas and chatting every day.
German verbs fall into three main groups: regular, irregular, and mixed. This mix makes German a lively language that needs focus and practice. Regular verbs have easy patterns, but irregular verbs offer a challenge with their unique forms.
Some of the most used German verbs are “sein” (to be), “haben” (to have), “werden” (to become), and “können” (to be able). These verbs are crucial for talking about actions, states, and abilities clearly.

Key Takeaways
- Learn the three categories of German verbs: regular, irregular, and mixed
- Focus on mastering core verbs like “haben” and “sein”
- Understand present tense verb endings: -e, -st, -t, and -en
- Practice conjugation patterns for different verb types
- Build a strong foundation with the most common German verbs
- Key Takeaways
- The Role of Verbs in Sentence Formation
- How Verbs Enable Expression in German
- Understanding Action Words and States of Being
- Können – Can/To Be Able To
- Müssen – Must/Have To
- Sollen – Should/Ought To
- Regular Verb Conjugation
- Irregular Verb Patterns
- Common Conjugation Mistakes to Avoid
- Movement and Travel Verbs
- Communication Verbs
- Daily Activity Verbs
- What are the most important German verbs to learn first?
- How do German verb conjugations work?
- What are modal verbs in German, and why are they important?
- How different are German verb tenses from English?
- What makes sein and haben so special in German?
- How can I improve my German verb usage?
- Are there any tricks to remembering German verb conjugations?
- What are the most useful action verbs for everyday German?
- How do German modal verbs differ from regular verbs?
- What's the best way to practice German verbs?
Why Learning German Verbs is Essential for Communication
Verbs are the heart of language, especially in German. They do more than just describe actions. Verbs like machen and kommen are key to good communication. They turn simple words into deep expressions.
Learning German verbs is not just about remembering words. It’s about grasping how these tools connect our thoughts. This enables us to communicate in a rich, detailed way.
The Role of Verbs in Sentence Formation
German sentences depend a lot on verb placement and how they change. Verbs like machen are crucial. They help shape our messages by:
- Showing the action or state
- Telling us about time and mood
- Linking different parts of a sentence
How Verbs Enable Expression in German
German verbs are very flexible. They can show:
- Physical actions (kommen, gehen)
- Feelings and emotions
- Mental processes
- Complex thoughts and plans
Understanding Action Words and States of Being
Not all verbs are about physical actions. Some describe feelings, thoughts, or abstract ideas. Getting good at these verbs lets us talk more clearly. It also helps us get the full picture of German culture and language.
The Basic Structure of German Verbs
German verbs have a unique structure that differs from English. Most common verbs end in -en or -n in their base form. This creates a clear pattern. For example, verbs like gehen (to go) and sehen (to see) follow this pattern.
It’s important to understand how verbs change. German verbs have many variations based on several factors:
- Person (ich, du, er/sie/es, wir, ihr, sie)
- Number (singular or plural)
- Tense (present, past, future)
- Verb type (regular or irregular)
When changing verbs like gehen or sehen, pay close attention to the endings. For example, in the present tense, the endings change with the subject:
- ich gehe (I go)
- du gehst (you go)
- er/sie/es geht (he/she/it goes)
The German verb system has eight main forms. These can be broken down into three or four main types. Regular verbs follow set patterns, while irregular verbs need more practice to remember. Learning these basics helps you use German verbs with confidence.
Top German Modal Verbs and Their Usage
German modal verbs are key in showing complex ideas and feelings. They help us talk about what we can do, must do, and want to do. Learning these verbs makes your German sound better and more natural.
Modal verbs change the meaning of the main verb. They add more to what you say. People use them a lot to share their feelings and needs.
Können – Can/To Be Able To
The verb können talks about what you can do. It shows you can do something. For example, “Ich kann Deutsch sprechen” means “I can speak German”.
- Expresses physical or mental ability
- Used to describe potential skills
- Indicates permission in some contexts
Müssen – Must/Have To
Müssen is for when you must do something. It shows you know you have to do it.
- Indicates strong personal or external requirements
- Expresses mandatory actions
- Demonstrates social or legal obligations
Sollen – Should/Ought To
Sollen is for when you think someone should do something. It’s great for giving advice or suggestions.
| Modal Verb | English Meaning | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Können | Can/Able | Ich kann schwimmen |
| Müssen | Must/Have to | Du musst arbeiten |
| Sollen | Should/Ought to | Sie soll früh schlafen |
Knowing these modal verbs makes your German better. You’ll talk more clearly and naturally.
Common Verbs in German: Essential Vocabulary
Learning common verbs in German is key for good communication. The German language uses specific verbs a lot. These verbs help us talk about our thoughts and what we want.
| English | German |
| Accept | Akzeptieren |
| Achieve | Erreichen |
| Admit | Zugeben |
| Affect | Beeinflussen |
| Agree | Zustimmen |
| Allow | Erlauben |
| Answer | Antworten |
| Appear | Erscheinen |
| Apologize | Sich entschuldigen |
| Argue | Streiten |
| Arrange | Arrangieren |
| Arrive | Ankommen |
| Ask (for something) | Bitten |
| Ask (a question) | Fragen |
| Attend | Besuchen |
| Avoid | Vermeiden |
| Become | Werden |
| Begin | Beginnen |
| Believe | Glauben |
| Borrow | Leihen |
| Break | Brechen |
| Breathe | Atmen |
| Bring | Bringen |
| Build | Bauen |
| Buy | Kaufen |
| Call | Rufen / Anrufen |
| Care | Sich kümmern |
| Carry | Tragen |
| Catch | Fangen |
| Cause | Verursachen |
| Change | Ändern |
| Check | Überprüfen |
| Choose | Wählen |
| Clean | Reinigen |
| Close | Schließen |
| Collect | Sammeln |
| Come | Kommen |
| Complain | Sich beschweren |
| Complete | Vervollständigen |
| Consist of | Bestehen aus |
| Concentrate | Sich konzentrieren |
| Congratulate | Gratulieren |
| Contain | Enthalten |
| Continue | Fortsetzen |
| Contribute | Beitragen |
| Control | Kontrollieren |
| Correct | Korrigieren |
| Cost | Kosten |
| Could | Könnte |
| Count | Zählen |
| Create | Erschaffen |
| Cross | Überqueren |
| Cry | Weinen |
| Cut | Schneiden |
| Damage | Beschädigen |
| Deal | Handeln |
| Deliver | Liefern |
| Deny | Leugnen |
| Describe | Beschreiben |
| Destroy | Zerstören |
| Develop | Entwickeln |
| Disappear | Verschwinden |
| Discover | Entdecken |
| Do | Tun / Machen |
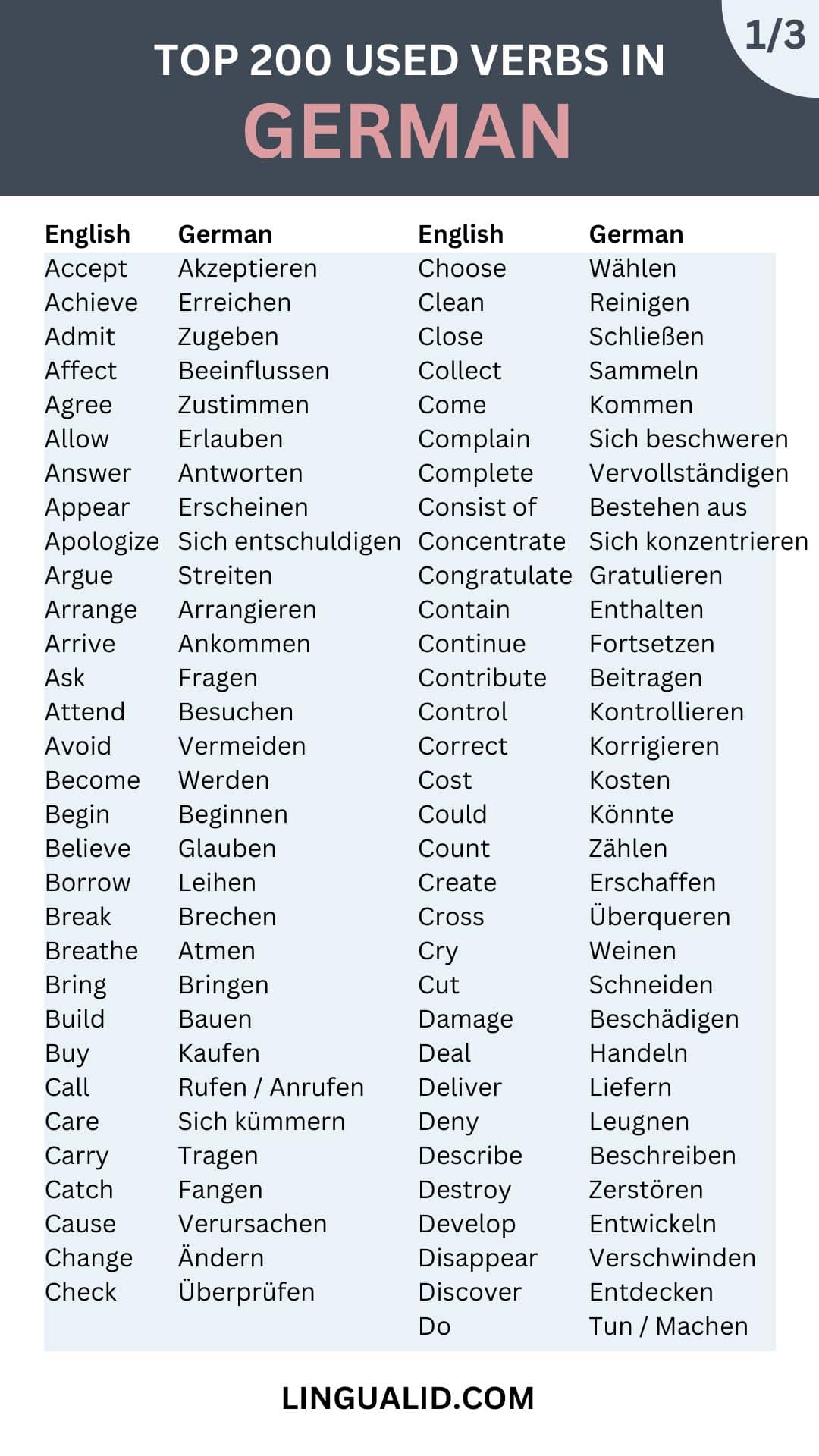
| Dress | Sich anziehen |
| Drink | Trinken |
| Drive | Fahren |
| Eat | Essen |
| Encourage | Ermutigen |
| Enjoy | Genießen |
| Exist | Existieren |
| Expect | Erwarten |
| Experience | Erleben |
| Explain | Erklären |
| Express | Ausdrücken |
| Face | Begegnen |
| Fall | Fallen |
| Feel | Fühlen |
| Fill | Füllen |
| Find | Finden |
| Finish | Beenden |
| Fly | Fliegen |
| Follow | Folgen |
| Forget | Vergessen |
| Forgive | Vergeben |
| Form | Formen |
| Give | Geben |
| Go | Gehen |
| Grow | Wachsen |
| Happen | Passieren |
| Have | Haben |
| Hear | Hören |
| Help | Helfen |
| Hide | Verstecken |
| Hold | Halten |
| Hope | Hoffen |
| Imagine | Sich vorstellen |
| Improve | Verbessern |
| Increase | Erhöhen |
| Influence | Beeinflussen |
| Inform | Informieren |
| Invite | Einladen |
| Keep | Behalten |
| Know | Wissen |
| Last | Dauern |
| Laugh | Lachen |
| Learn | Lernen |
| Leave (a place) | Verlassen |
| Leave (something/someone) | Lassen |
| Lend | Leihen |
| Like | Mögen |
| Limit | Begrenzen |
| Listen | Zuhören |
| Live | Leben |
| Look | Schauen |
| Look for | Suchen |
| Lose | Verlieren |
| Love | Lieben |
| Make | Machen |
| Measure | Messen |
| Meet | Treffen |
| Move | Bewegen |
| Need | Brauchen |
| Offer | Anbieten |
| Open | Öffnen |
| Order | Bestellen |
| Paint | Malen |
| Pay | Zahlen |
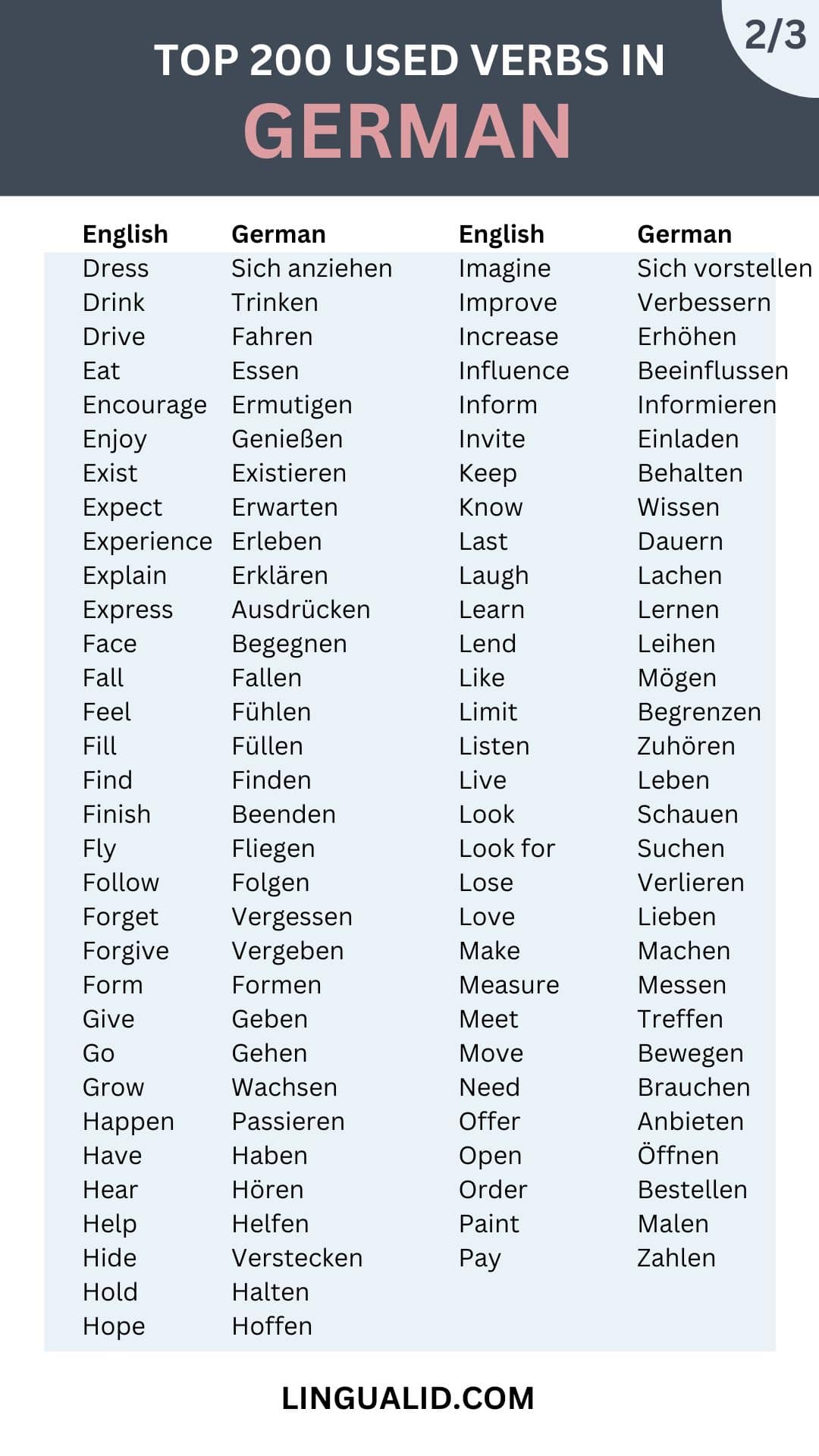
| Play | Spielen |
| Pray | Beten |
| Prefer | Bevorzugen |
| Prepare | Vorbereiten |
| Press | Drücken |
| Prevent | Verhindern |
| Produce | Produzieren |
| Protect | Schützen |
| Provide | Bereitstellen |
| Push | Drücken / Schieben |
| Reach | Erreichen |
| Read | Lesen |
| Receive | Erhalten |
| Record | Aufzeichnen |
| Reduce | Reduzieren |
| Release | Freigeben |
| Remember | Erinnern |
| Remove | Entfernen |
| Repeat | Wiederholen |
| Replace | Ersetzen |
| Reply | Antworten |
| Resist | Widerstehen |
| Return | Zurückkehren |
| Reveal | Enthüllen |
| Run | Laufen |
| Say | Sagen |
| See | Sehen |
| Sell | Verkaufen |
| Send | Senden |
| Sew | Nähen |
| Share | Teilen |
| Show | Zeigen |
| Sing | Singen |
| Sit | Sitzen |
| Sleep | Schlafen |
| Smile | Lächeln |
| Speak | Sprechen |
| Start | Beginnen |
| Study | Studieren |
| Succeed | Erfolg haben |
| Suggest | Vorschlagen |
| Supply | Liefern |
| Suppose | Annehmen |
| Survive | Überleben |
| Swear | Schwören |
| Swim | Schwimmen |
| Take | Nehmen |
| Talk | Reden |
| Taste | Schmecken |
| Teach | Lehren |
| Tell | Erzählen |
| Thank | Danken |
| Think | Denken |
| Throw | Werfen |
| Touch | Berühren |
| Train | Trainieren |
| Translate | Übersetzen |
| Travel | Reisen |
| Treat | Behandeln |
| Trust | Vertrauen |
| Try | Versuchen |
| Turn | Drehen |
| Understand | Verstehen |
| Use | Benutzen |
| Visit | Besuchen |
| Wait | Warten |
| Wake up | Aufwachen |
| Walk | Gehen |
| Want | Wollen |
| Watch | Anschauen |
| Wear | Tragen |
| Win | Gewinnen |
| Wonder | Sich wundern |
| Work | Arbeiten |
| Write | Schreiben |
We have a list of 200 essential German verbs. These verbs will make your language skills better. They cover everything from simple actions to complex ideas.
- Top 5 Most Frequently Used Verbs:
- Sein (to be)
- Haben (to have)
- Werden (to become)
- Können (can)
- Müssen (must)
About 45% of these verbs are irregular. This means learners need to focus on their special forms. The verb “denken” lets you share your thoughts. “Möchten” is for polite requests and wishes.
| Verb Category | Percentage | Number of Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Necessity/Obligation Verbs | 15% | 3 |
| Ability Verbs | 5% | 1 |
| Desire/Preference Verbs | 10% | 2 |
By learning these verbs, you can talk confidently in German. Each verb lets you express different actions, states, and plans. They are vital for your language skills.
Present Tense Conjugation Patterns
Learning German verb conjugation is key to good communication. The present tense is essential for talking about actions, plans, and ongoing situations in German.
Changing verb endings based on the subject is a big part of German verb conjugation. This is different from English, where each pronoun needs its own verb ending.
Regular Verb Conjugation
Regular verbs in German have a simple pattern. To change them, remove the infinitive ending and add the right one:
- ich: -e
- du: -st
- er/sie/es: -t
- wir: -en
- ihr: -t
- sie/Sie: -en
Irregular Verb Patterns
Irregular verbs like haben and sein have their own rules. For example, the verb sein (to be) changes like this:
| Pronoun | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| ich | bin |
| du | bist |
| er/sie/es | ist |
| wir | sind |
| ihr | seid |
| sie/Sie | sind |
Common Conjugation Mistakes to Avoid
When learning German verbs, avoid these common mistakes:
- Forgetting to change verb stems for irregular verbs
- Mixing up endings for different pronouns
- Neglecting pronunciation changes with stem-changing verbs
Practice and patience are key to mastering German verb conjugations!
Sein and Haben: The Foundation Verbs
In German, “sein” (to be) and “haben” (to have) are key verbs. They are the foundation of the language. They are used as main verbs and help in forming different tenses.
“Sein” is a complex verb. It is the most irregular in German. It has unique ways of changing its form. Let’s look at its present tense:
- 1st Person Singular: ich bin
- 2nd Person Singular: du bist
- 3rd Person Singular: er/sie/es ist
- 1st Person Plural: wir sind
- 2nd Person Plural: ihr seid
- 3rd Person Plural: sie sind
“Haben” is a bit easier but still has its own challenges. Its present tense forms are:
- 1st Person Singular: ich habe
- 2nd Person Singular: du hast
- 3rd Person Singular: er/sie/es hat
- 1st Person Plural: wir haben
- 2nd Person Plural: ihr habt
“Sein” and “haben” are crucial for making compound tenses. “Sein” goes with verbs of movement or change. “Haben” works with most verbs that take an object. Knowing these verbs helps understand German grammar better.
Action Verbs for Everyday Situations
Learning common verbs in German makes talking easier. These words help you share your actions, thoughts, and daily life with others.
Verbs like machen, kommen, and gehen are key for everyday talks. They let you talk about what you do, what you plan, and connect with others.
Movement and Travel Verbs
Movement verbs are great for talking about your travels and actions. Here are some important ones:
- Gehen (to go) – basic for talking about walking or moving
- Kommen (to come) – key for saying you’ve arrived
- Fahren (to drive/travel) – used for getting around
- Reisen (to travel) – for longer trips
Communication Verbs
Communication verbs are vital for talking and sharing thoughts:
- Sprechen (to speak) – essential for conversations
- Sagen (to say) – for sharing statements
- Fragen (to ask) – important for asking questions
Daily Activity Verbs
Everyday verbs are great for talking about your daily life and experiences:
- Machen (to do/make) – useful for many activities
- Arbeiten (to work) – for talking about your job
- Lernen (to learn) – for sharing about school or learning
Learning these action verbs will boost your German skills. You’ll feel more confident in daily conversations.
Past Tense Forms of Common German Verbs
Learning past tense forms is key to mastering German verbs. German has two main past tense forms: the simple past (Präteritum) and the present perfect (Perfekt). Each form has its own way to show that an action is done.
Verbs like sehen (to see) and sagen (to say) show interesting patterns. Regular verbs change in a predictable way. But irregular verbs need extra attention.
- Simple Past (Präteritum): Used more in written German
- Present Perfect (Perfekt): Better for spoken conversations
- Conjugation involves specific verb endings
Regular verb conjugation has standard endings:
- -te for ich, er/sie/es
- -test for du
- -ten for wir, Sie, sie (plural)
- -tet for ihr
The verb sagen changes in the past tense like this:
ich sagte (I said)
du sagtest (you said)
er/sie/es sagte (he/she/it said)
Knowing these patterns helps learners talk about past events in German.
Using German Verbs in Practical Conversations
Learning common German verbs makes language learning real. Verbs like “wissen” (to know) and “denken” (to think) are key for sharing thoughts and info. They help learners move from studying to speaking with confidence.
Knowing when and how to use verb forms is crucial. For example, “Ich weiß” (I know) fits many situations, from being sure to sharing facts. “Denken” lets you share opinions, like “Was denkst du?” (What do you think?), which is vital for good talks.
German verb use is more than just translating. Native speakers use idioms and specific verb uses that need more than just knowing the words. Learning these helps learners sound natural and connect better with Germans in real life.
Video lessons, language apps, and talking with others are great for learning verb skills. By getting into real German talks, you’ll learn to use verbs smoothly. This turns book knowledge into easy, confident talking.
FAQ
What are the most important German verbs to learn first?
How do German verb conjugations work?
What are modal verbs in German, and why are they important?
How different are German verb tenses from English?
What makes sein and haben so special in German?
How can I improve my German verb usage?
Are there any tricks to remembering German verb conjugations?
What are the most useful action verbs for everyday German?
How do German modal verbs differ from regular verbs?
What’s the best way to practice German verbs?
Oualid Cheddadi is the founder of Lingualid, a platform that inspires independent language learners worldwide, regardless of the language they are learning. The name “Lingualid” is derived from the Portuguese word for “language,” “língua,” and the last three letters of Oualid’s name, “Lid.”