The Japanese language is truly unique and captivating. It is spoken by over 128 million people worldwide, making it the 9th most common language. It’s the official tongue of Japan and also found in communities in Korea, Taiwan, and the U.S.

Japanese belongs to the Japonic family and stands alone as a language isolate. Yet, it has been deeply shaped by Chinese, especially in writing and vocabulary. The language’s history is long, from adopting Chinese writing in the 4th century to its own distinct sound and writing systems later on.
Today, Japanese is famous for its complex writing system. It uses three scripts: kanji, hiragana, and katakana. Its grammar and pronunciation are also quite different from English.
Key Takeaways
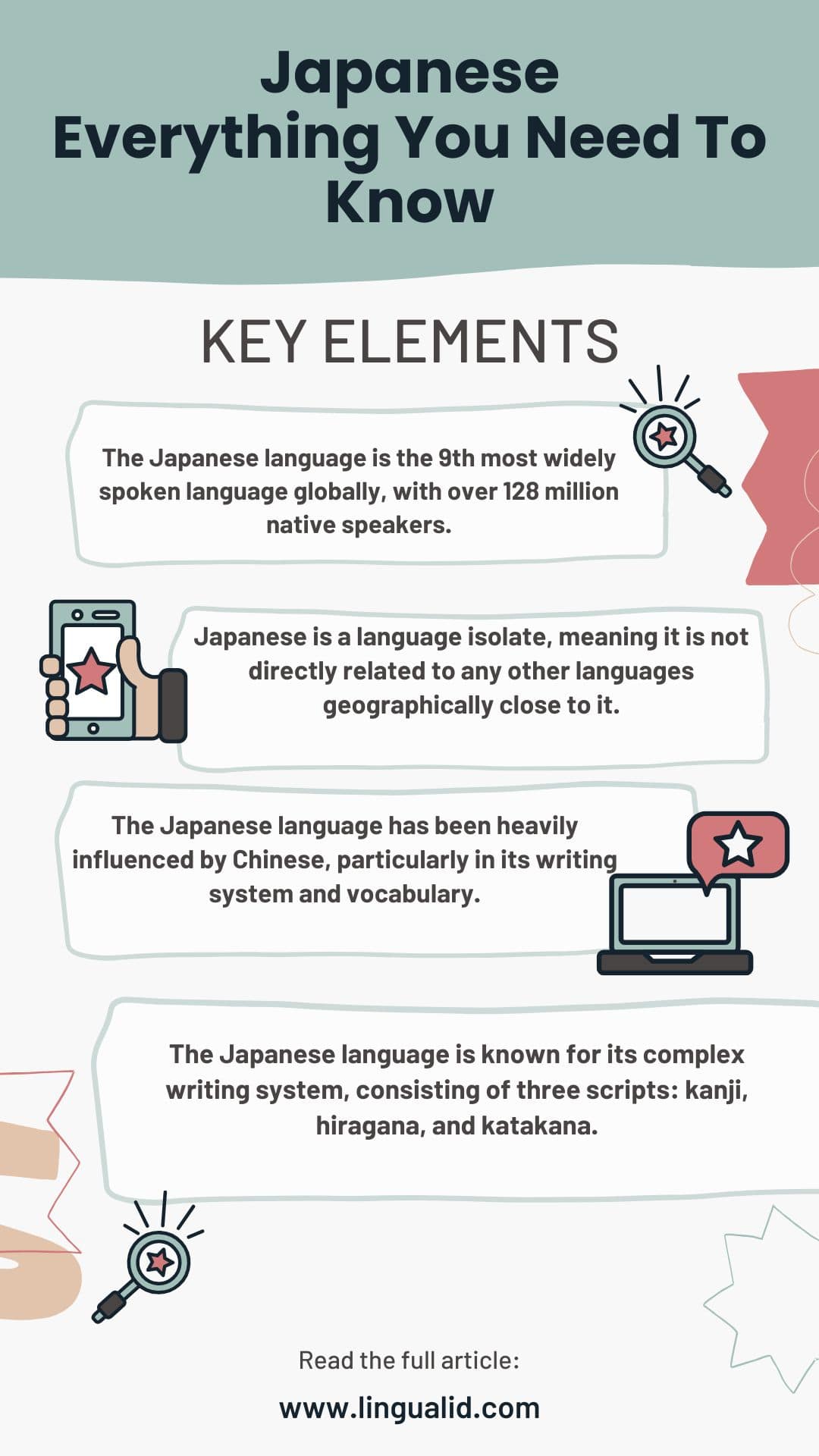
- The Japanese language is the 9th most widely spoken language globally, with over 128 million native speakers.
- Japanese is a language isolate, meaning it is not directly related to any other languages geographically close to it.
- The Japanese language has been heavily influenced by Chinese, particularly in its writing system and vocabulary.
- The Japanese language is known for its complex writing system, consisting of three scripts: kanji, hiragana, and katakana.
- The Japanese language has a unique grammar structure and pronunciation compared to English.
- Key Takeaways
- What Language Family Is Japanese In?
- The History of the Japanese Language
- Chinese Influence on Japanese
- Kanji: The Borrowed Characters
- Hiragana: The Indigenous Syllabary
- Katakana: The Adopted Script
- Is Japanese a "Hard" Language?
- Zero Knowledge of Japanese
- Basic Japanese Pronunciation
- Learning to Type Hiragana in Japanese
- Beginning Kanji & Stockpiling Kanji Knowledge
- Learning to Type Katakana
- Learning to Type Kanji
- What Language Family Is Japanese In?
- What is the History of the Japanese Language?
- How Has Chinese Influenced the Japanese Language?
- What are the Three Writing Systems Used in Japanese?
- What are the Different Japanese Dialects?
- What is the Phonology of the Japanese Language?
- Is Japanese a "Hard" Language to Learn?
- What is the Cultural Significance of the Japanese Language?
- What are the Key Terms in the Japanese Language?
- Where Should I Start When Learning Japanese?
- What is the Concept of "Kanji"?
- How Do I Progress in Learning the Japanese Language?
Basic Facts About the Japanese Language
The Japanese language is both fascinating and complex. It has caught the eye of scholars and fans around the world. Its unique origins, rich history, and cultural influences make it a treasure trove of linguistic diversity.
What Language Family Is Japanese In?
Japanese is a “language isolate,” meaning it doesn’t fit into any known language family. This mystery has sparked many theories. Some believe it came from the Yayoi people from Korea, while others think it evolved from the indigenous Jomon people already in the area.
The History of the Japanese Language
The earliest written records of Japanese date back to the 8th century. Its grammar has stayed relatively consistent over the years. The language has gone through several periods, including Old Japanese, Late Old Japanese, Middle Japanese, Early Modern Japanese, and Modern Japanese. Each period has its own distinct features and developments.
Chinese Influence on Japanese
The Chinese language has had a big impact on Japanese. Over time, Japanese has taken on many Chinese loanwords, known as “Sino-Japanese” vocabulary. It also adopted the Chinese writing system, called Kanji. This has greatly influenced Japanese’s vocabulary and written form.
| Key Fact | Statistic |
|---|---|
| Japanese Language Family | Classified as a “language isolate” |
| Kanji Characters Required to Read a Newspaper | Over 2,000 |
| Possible Pronunciations for a Single Kanji Character | More than 10 |
| Japanese Language Speakers Worldwide | Over 128 million |
The History of the Japanese Writing System
The Japanese writing system is a mix of several scripts, each with its own history. At its heart are Kanji, Hiragana, and Katakana. These three scripts together form the written Japanese language.
Kanji: The Borrowed Characters
Kanji, borrowed from Chinese, is key to the Japanese script. By 2010, students needed to learn over 2,136 Kanji characters. More than 50,000 Kanji are used daily, for both Japanese and Chinese words.
Hiragana: The Indigenous Syllabary
Hiragana is a unique Japanese syllabary that started in the Heian period (794-1185). It’s a simpler version of Kanji. It has 46 basic characters and is used for grammar, particles, and Japanese words.
Katakana: The Adopted Script
Katakana also began in the Heian period in the 9th century. It’s mainly for foreign words, names, and technical terms. Like Hiragana, it has 46 basic characters.
The mix of Kanji, Hiragana, and Katakana shows the Japanese language’s deep history and cultural influences. This complex system keeps changing, showing the Japanese language’s dynamic nature.
Related: Top Reasons To Learn Japanese
Japanese Dialects
Japan has a standard Japanese dialect based on the Tokyo accent, called kyōtsūgo. But, the country also has many regional dialects. Each one has its own special features, showing the rich linguistic and geographic diversity of Japan.
The Kansai dialect is famous for its use in comedy. The Tōhoku dialect is harder for others to understand. Meanwhile, the Okinawa dialect shows the Ryukyuan languages’ influence. These regional dialects are fading due to education, media, and travel. Yet, they remain key to Japanese culture and identity.
Japan’s Japanese dialects fall into four main groups: Eastern Japanese, Western Japanese, Kyushu Japanese, and the Hachijo dialect. Each has its own pitch-accent, grammar, and words. This makes them unique and interesting parts of the Japanese language.
“The dialects of the Japanese language are primarily divided into Eastern (including modern capital Tokyo) and Western (including old capital Kyoto) clades, with additional branches found in Kyushu and Hachijō Island.”
Even though the government pushes for a standard Japanese language, the regional dialects are still vital to Japan’s culture and language. These Japanese dialects give us a peek into Japan’s history and the unique identities of its regions. They make the Japanese language both diverse and captivating.
The Phonology of the Japanese Language
The Japanese language has a simple sound system compared to English. It has five vowel sounds: /a/, /e/, /i/, /o/, and /u/. These vowels are easy to learn for those who are not native speakers.
Japanese also has palatalized sounds made by adding small letters like や, ゆ, or よ to consonants. It uses a pitch accent system to change word meanings, similar to English stress patterns.
| Japanese Vowels | Example Words |
|---|---|
| /a/ | あ (a) |
| /e/ | え (e) |
| /i/ | い (i) |
| /o/ | お (o) |
| /ɯ/ | う (u) |
Japanese phonology includes at least 12 distinct consonants. Some studies say there could be up to 21 consonants. The voiceless stops (/p/, /t/, /k/) are different in voice onset time from English and Spanish.
The Japanese phonology is straightforward with clear vowels and unique consonants. To get better at Japanese, it’s important to practice regularly.
Learning the Japanese Language
The Japanese language is often seen as hard for English speakers. But, it’s actually more accessible than you might think. There are many aspects that make it easier to learn.
Is Japanese a “Hard” Language?
The Japanese writing system is unique. It uses kanji (Chinese characters), hiragana, and katakana. The language’s complex grammar and honorifics can be tough for beginners.
But, Japanese has features that help learners. Its pronunciation is consistent, and grammar rules are mostly straightforward. This makes it easier to understand and use.
The Japan Foundation helps language learners. They offer training programs and Japanese-language courses. They also create online and audio-visual materials for learners around the world.
Learning Japanese is different for everyone. It depends on your past language experience, how you learn, and how much you practice. With the right tools and effort, many can become proficient in Japanese.
The Beauty of the Japanese Language
The Japanese language is seen as one of the most beautiful and unique in the world. Its rich history and deep cultural significance make it special. It is closely linked to Japanese traditions and values.
The Japanese language has a unique writing system. It uses kanji, hiragana, and katakana scripts. This mix of characters adds visual elegance and reflects cultural nuances over centuries.
The Japanese language is also known for its sophisticated system of politeness. It has different levels of formality and respect. This shows the cultural values of Japanese society, like harmony, respect, and consideration.
The Japanese language has a rich tapestry of onomatopoeic words. These words capture sounds, sensations, and emotions. They add to the beauty and expressiveness of the language, allowing for precise and nuanced expression.
The beauty of the Japanese language comes from its intricate interplay of cultural, linguistic, and aesthetic elements. It captivates the senses and invites deeper exploration of its uniqueness and cultural significance.
Japanese Language
The Japanese language, also known as Nihongo, is spoken by most people in Japan. The people of Japan are called Nihonjin, and their country is Nihon or Nippon. With about 123 million native speakers, the Japanese language is rich and interesting.
The Japanese language belongs to the Japonic family, which also includes Ryukyuan and Hachijō languages. Scholars debate its origins, but it’s clear that Chinese has influenced it. The earliest Japanese words date back to the 3rd century AD. Over time, the language has grown, with Chinese and European words adding to its vocabulary.
| Language Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Classification | Japanese is an agglutinative, mora-timed language with a lexically significant pitch-accent |
| Writing System | Japanese uses a combination of Chinese characters, hiragana, katakana, and Latin script |
| Dialects | Japanese has various regional dialects, with the standard dialect based on the Tokyo dialect |
| Loanwords | Japanese has incorporated many loanwords from languages such as English, German, Portuguese, and others, particularly in the areas of technology and modern life |
The Japanese language has a long and varied history. It’s both ancient and modern, making it fascinating. It’s a key part of Nihonjin culture and identity.
Order of Learning Japanese
Starting your journey to learn Japanese is exciting. It’s key to begin with the basics. Whether you know nothing or a bit, learning Japanese follows a clear path. This ensures you have a strong base.
Zero Knowledge of Japanese
At the start, learn the basics if you know nothing. Get to know the Japanese writing systems. This includes Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji. Also, focus on Japanese pronunciation basics.
Basic Japanese Pronunciation
Understanding Japanese sounds is vital. Learn the language’s vowels and consonants. Practice speaking and listening to improve your skills.
Learning to Type Hiragana in Japanese
Start by learning to type Hiragana. It’s the basic writing system. Hiragana has 46 characters that show the language’s sounds. Knowing Hiragana lets you read and write simple Japanese words.
By following this order, learners of Japanese can build a solid foundation. Then, they can move on to more complex parts of the language. This includes Katakana, Kanji, and improving speaking, reading, and writing skills.
Understanding the Concept of “Kanji”
The Japanese language has a unique writing system called kanji. These Chinese characters are a big challenge for many learners. But, knowing about kanji is key to really understanding Japanese.
Kanji is a big part of the Japanese writing system, with about 2,000 characters. In comparison, hiragana and katakana have only 46 characters each. This shows how complex and rich kanji is, shaped by Japan’s history and culture.
The Japanese writing system shows how the language has evolved. Kanji lets people express complex ideas that are hard to say with hiragana and katakana.
Learning kanji is a lifelong journey for many Japanese speakers. It starts in elementary school and goes on through school. The Jōyō Kanji list, with 2,136 essential characters, is a key to reading Japanese well.
As learners get better at kanji, they understand Japanese better. Kanji shows the beauty of the Japanese writing system and its deep connection to Chinese characters.
Progression in the Japanese Language
As learners move forward in Japanese, they build on what they’ve learned. This includes mastering the writing systems. The path to becoming proficient in Japanese has many milestones, each with its own challenges and rewards.
Beginning Kanji & Stockpiling Kanji Knowledge
Mastering kanji, the logographic characters from Chinese, is a big challenge. It takes years of hard work to learn them. By stockpiling kanji knowledge, students can grow their vocabulary and improve their reading and writing.
Learning to Type Katakana
The Japanese writing system also includes katakana, used for foreign words. Learning to type katakana is crucial. It helps learners read and write various texts and talk with native speakers.
Learning to Type Kanji
The last step is mastering typing kanji. This skill boosts your writing and deepens your understanding of kanji. Being able to type kanji opens doors to writing emails and joining online discussions with Japanese people.
The journey through Japanese is full of challenges and rewards. By focusing on learning kanji, typing katakana, and typing kanji, learners can make steady progress. They’ll gain a deeper understanding and mastery of this fascinating language.
Conclusion
Learning Japanese is a rewarding journey that opens a window into Japan’s vibrant culture. It’s not as hard as many think, thanks to its simple sounds and logical grammar.
We’ve looked at the Japanese language’s history, writing systems, and dialects. Understanding these basics lets learners dive into a world of cultural immersion and personal growth.
Whether you’re new to Japanese or already know it well, the key is to be open-minded and eager to practice. This approach will open doors to better communication and a deeper understanding of Japanese culture.
FAQ
What Language Family Is Japanese In?
Japanese belongs to the Japonic language family. It’s considered a language isolate. This means it’s not closely related to nearby languages.
What is the History of the Japanese Language?
The first written Japanese dates back to the 8th century. Two writing styles were used then: Kanbun and Man’yogana. Kanbun was in Classical Chinese style, and Man’yogana used Chinese characters for Japanese sounds.
Using Chinese characters for Japanese was hard. So, the unique Japanese writing system of hiragana and katakana was developed.
How Has Chinese Influenced the Japanese Language?
Chinese has greatly influenced Japanese. This is especially true in writing and vocabulary.
What are the Three Writing Systems Used in Japanese?
Japanese uses three scripts: kanji, hiragana, and katakana.
What are the Different Japanese Dialects?
Japan has a standard dialect, known as kyōtsūgo. But, there are many regional dialects too. The Kansai dialect is famous in comedy, while the Tōhoku dialect is harder to understand. The Okinawa dialect shows Ryukyuan language roots.
What is the Phonology of the Japanese Language?
Japanese phonology is simple, unlike English. It has only 5 vowels: a, e, i, o, and u. These vowels are clear and easy to pronounce.
Is Japanese a “Hard” Language to Learn?
Many think Japanese is hard for English speakers. But, it’s actually easier than it seems. Japanese has many features that make it accessible.
What is the Cultural Significance of the Japanese Language?
Japanese is seen as a beautiful and unique language. Its history and cultural ties make it special. It reflects Japanese traditions and values.
What are the Key Terms in the Japanese Language?
The Japanese language is called Nihongo. People from Japan are Nihonjin. The country is Nihon or Nippon.
Where Should I Start When Learning Japanese?
Beginners should start with the basics. This includes pronunciation, writing systems, and basic vocabulary.
What is the Concept of “Kanji”?
Kanji, or Chinese characters, are a big challenge for beginners. They are a key part of the Japanese writing system.
How Do I Progress in Learning the Japanese Language?
As you learn more, focus on building on what you’ve learned. Pay special attention to the writing systems.
Oualid Cheddadi is the founder of Lingualid, a platform that inspires independent language learners worldwide, regardless of the language they are learning. The name “Lingualid” is derived from the Portuguese word for “language,” “língua,” and the last three letters of Oualid’s name, “Lid.”