Russian is a key language with 265 million speakers worldwide, ranking it the 7th most spoken. It’s one of the six UN languages, showing its global importance. It’s official in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan. It also has regional status in Ukraine, Georgia, Romania, and Moldova.
In Central Europe, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe, Russian is the main language among former Soviet states. It’s the top Slavic language, with 155 million native speakers.
Key Takeaways
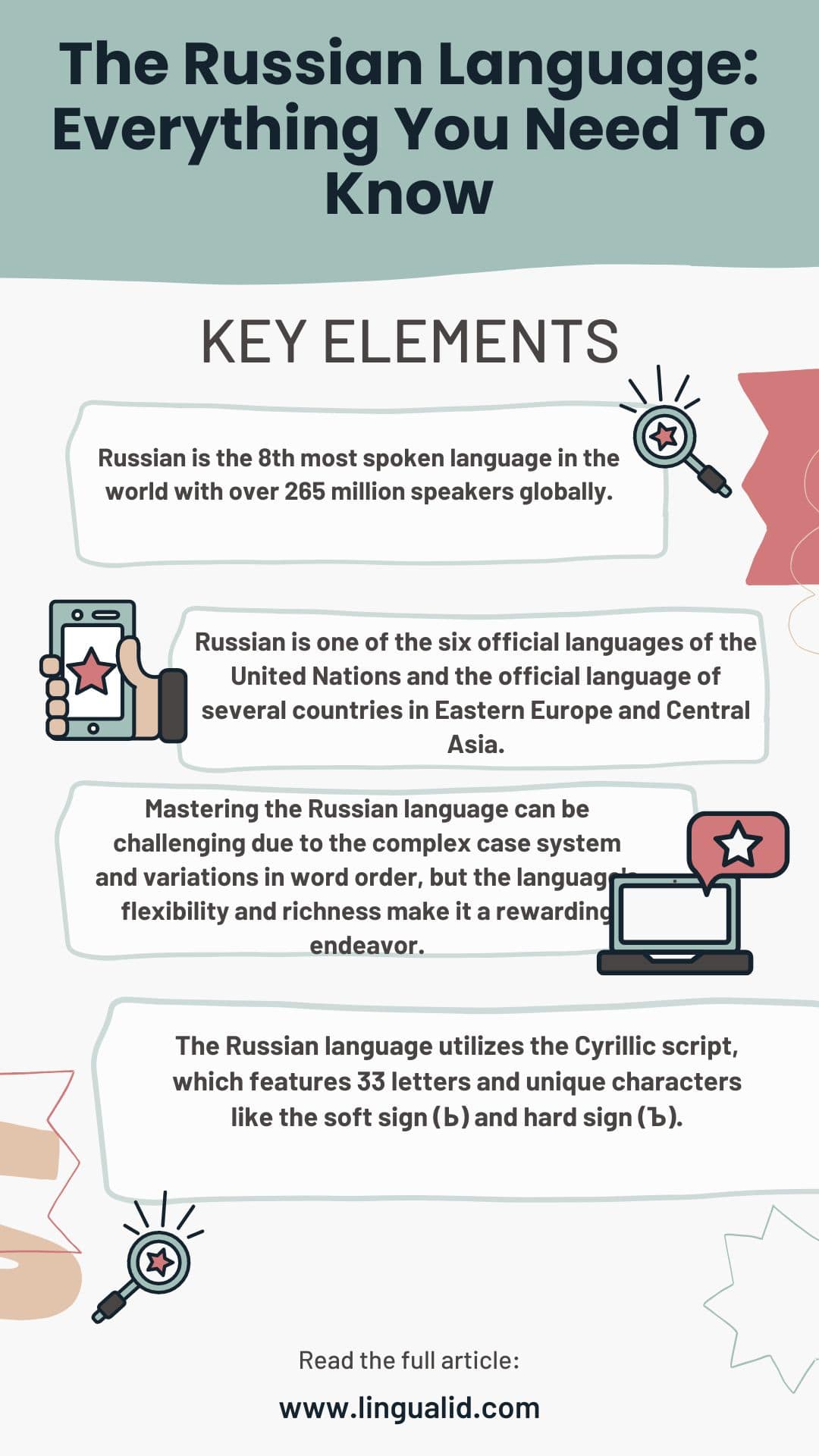
- Russian is the 7th most spoken language in the world with over 265 million speakers globally.
- Russian is one of the six official languages of the United Nations and the official language of several countries in Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
- Russian is the most widely spoken Slavic language, with 155 million native speakers.
- The Russian language utilizes the Cyrillic script, which features 33 letters and unique characters like the soft sign (Ь) and hard sign (Ъ).
- Mastering the Russian language can be challenging due to the complex case system and variations in word order, but the language’s flexibility and richness make it a rewarding endeavor.
- Key Takeaways
- Importance and Prevalence of Russian
- Where Russian is Spoken
- The Russian Language Through Changes of States
- Pushkin: the Father of Modern Russian Language
- How to Pronounce Russian Words
- Voiced and Voiceless Consonants in Russian
- The Writing System
- Cases
- Word Order
- How important and prevalent is the Russian language?
- Where is Russian spoken?
- What language family does Russian belong to?
- How did the Russian language develop historically?
- How did the Russian language change in the 20th century?
- What is the Russian alphabet and writing system like?
- How are consonants pronounced in Russian?
- What are the vowel sounds in Russian?
- What are some key challenges for English speakers learning Russian?
Basic Facts About the Russian Language
The Russian language is crucial and widely spoken, with a huge global presence. It has about 258 million speakers worldwide, making it the 8th most spoken language. It’s the main language in Russia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan. It also has special status in Ukraine, Georgia, Romania, and Moldova.
Importance and Prevalence of Russian
Russian is key in Central Europe, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe, especially in the former Soviet areas. It’s one of the six official UN languages. This shows its big role on the world stage.
Where Russian is Spoken
- Russia: 154 million native speakers
- Worldwide: 258 million total speakers
- Eighth most-spoken language globally
- Official language in 4 countries: Russia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan
- Widely used as a second language in former Soviet republics
The Russian language has a deep history and has been crucial in Eurasia’s culture and politics for centuries. Its widespread use and importance make it key to learn and study.
What Language Family is Russian In?
The Russian language belongs to the Slavic language family. This family is part of the Indo-European language family. So, Russian is very close to languages like Ukrainian and Belarusian.
Russian is the most spoken and most relevant Slavic language today. There are over 150 million native Russian speakers. Plus, 110 million speak it as a second language. This makes a total of more than 258 million Russian speakers worldwide.
Russian is the seventh-largest language in the world by speakers. It’s after English, Mandarin, Hindi-Urdu, Spanish, French, and Arabic. It’s also one of the six official languages of the United Nations. Russia has over 100 minority languages, with 35 considered official in different areas.
- Russian is the most spoken native language in Europe.
- Russian is the most spoken Slavic language.
- Approximately 30% of the Russian population can speak English.
The History of the Russian Language
The Russian language has a long and fascinating history. It started from the Proto-Slavic language in the 5th century CE. This language split into three branches: West Slavic, South Slavic, and East Slavic. The East Slavic branch led to the modern Russian language.
The Russian Language Through Changes of States
In the 14th century, Russia was free from Mongol rule. It was then split into two states: the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow. The Grand Duchy of Moscow would become the root of modern Russian.
By the late 1500s, Russian had become its own language. It took words from Polish and German and grew its vocabulary. Over time, Russian changed a lot, especially in the 18th and 19th centuries. This was when the Russian Empire grew and foreign words came into the language.
Pushkin: the Father of Modern Russian Language
Alexander Pushkin was a key figure in shaping the Russian language. Known as the “Father of Modern Russian Literature,” his works helped make Russian a standard language. He made it a powerful tool for art.
From its beginnings to today, the Russian language has shown its strength and ability to change. Now, Russian is a major language worldwide, spoken by millions. It’s also in high demand for translation and interpretation services.
Related post: Top Reasons To Learn Russian
Changes in the Russian Language in the 20th Century
The 20th century was a big change for the Russian language. Russia became a world leader through two wars and the Cold War. This made the spread of the Russian language grow fast across the old Soviet states. Russian became key in education and government in these new countries.
The standardization of Russian got better during this time. With more media in the second half of the century, the standard language spread more. This led to regional dialects becoming less common. Now, standard Russian is the main way people talk across Russia.
A big event that changed the 20th century changes in the Russian language was the 1918 Russian Orthographic Reform. The Bolsheviks brought it in to make writing easier and boost reading skills in the Soviet Union. It got rid of some extra letters and made the language closer to everyday speech.
| Key Changes in the 1918 Russian Orthographic Reform | Impact |
| Replacing Ѣ with Е due to vowel merger | Streamlining the writing system |
| Removing the letter ъ that had lost its sound-distinguishing function | Eliminating redundant signs, leading to cost savings in the printing industry |
Some émigré groups criticized the reform, seeing it as a break from tradition. Yet, it was key in making the Russian language more standard and boosting literacy in the Soviet era.
Russian Alphabet and Writing System
The Russian language uses the Cyrillic alphabet, which came from the Greek script with Latin touches. It has 33 letters, with 20 consonants, 10 vowels, and a few more. Most Cyrillic letters are different from their Latin versions and need careful learning.
How to Pronounce Russian Words
Getting Russian words right is key to speaking the language well. The Russian alphabet has 21 consonants, with 15 that can be pronounced two ways – hard or soft. Whether a consonant sounds soft or hard depends on the next letter. Also, there are pairs of consonants with different sounds.
- The Russian Cyrillic alphabet has 33 letters, including 20 consonants, 10 vowels, a semivowel/consonant, and two modifier letters.
- The oldest Russian alphabet dates back to the 10th century and changed to its current form in 1918.
- Letters were removed over time, with some gone before 1750 and others changed between 1917-18.
Knowing the Russian alphabet and Russian pronunciation is key to speaking the Russian writing system well. Mastering these basics helps learners speak Russian with more confidence.
Russian language
The Russian language has a complex consonant system with 21 different consonants. It’s known for its unique feature of palatalization. This means certain consonants change sound when followed by specific vowels or the soft sign.
Palatalization is key to understanding Russian consonant pronunciation. Out of 21 consonants, 15 have two sounds – hard and soft. Whether a consonant sounds soft or hard depends on the next letter.
Voiced and Voiceless Consonants in Russian
Russian also has a special system of Russian voiced and voiceless consonants. Voiced consonants like “б” (b) and “д” (d) vibrate the vocal cords. Voiceless consonants, such as “п” (p) and “т” (t), don’t vibrate.
This difference in consonants changes the meaning of words in Russian. For example, “сад” (sad, garden) and “сат” (sat, sat) only differ in the final consonant’s voicing.
Learning to pronounce Russian consonants correctly is vital for language proficiency. With practice, learners can master the complex sounds of Russian and communicate well.
Vowels in the Russian Language
Learning the Russian vowel pronunciation is key to mastering Russian. The Russian alphabet has 33 letters, with 21 consonants and 10 vowels. These 10 letters represent the 6 basic Russian vowel sounds. Knowing how to pronounce these vowels is vital for speaking Russian well.
Russian vowels fall into two groups: hard and soft. Hard vowels (А, О, У, Ы, and Э) make a hard sound, while soft vowels (Я, Ё, Ю, И, and Е) make the previous consonant soft. Here are some important facts about Russian vowels:
- The letter У always sounds the same, whether stressed or unstressed.
- Ы is a unique vowel in Russian, sounding like a cross between “ee” and “ooh”.
- The letter Я sounds the same when stressed and unstressed, pronounced as “ya”.
- The letter Ё sounds the same whether stressed or unstressed, pronounced as “yo”.
- Ю is stronger when stressed, while its pronunciation softens when unstressed.
- The letter И sounds shorter when unstressed and longer when under stress.
- The letter Е sounds different when under stress (ye) compared to when unstressed (i).
Getting the hang of Russian vowel pronunciation is key to speaking Russian fluently. By learning the 6 basic Russian vowel sounds and their unique traits, learners can speak with confidence. This helps them communicate well with native speakers.
Learning the Russian Language
Learning Russian can be both rewarding and challenging for English speakers. It involves understanding the Cyrillic writing system and the complex case structure. But, with regular practice, the flexible word order can make it easier.
The Writing System
The Cyrillic alphabet used in Russian might seem hard at first if you’re used to the Latin script. Yet, with effort and practice, you can get the hang of it. Tools like audio lessons and vocabulary exercises can help you learn the Cyrillic letters and their sounds.
Cases
Mastering the Russian case system is one of the biggest challenges. Nouns, pronouns, and adjectives change form based on their sentence role. It takes time and effort, but knowing the cases is key to making correct sentences.
Word Order
Russian sentences can be more flexible than English ones. While the usual order is subject-verb-object, you can change the word order to add meaning or stress. This flexibility can help balance out the difficulties of the case system.
Learning the Russian language takes patience and hard work, but it’s worth it. With structured lessons, lots of practice, and real-life language materials, learning Russian can be both fun and rewarding.
Conclusion
The Russian language is a treasure full of history and variety. It has a long past and many different ways of speaking. From its Slavic roots to today, Russian takes learners on an exciting journey through culture and knowledge.
Learning Russian can be tough, with its complex grammar and Cyrillic letters. But diving into it through reading, listening, and speaking can make you proficient. It also helps you appreciate this global language more.
Knowing about Russian’s history, different dialects, and how it’s used today helps us understand the Russian people better. It opens doors to exploring literature, politics, business, or just enjoying linguistic diversity. Russian offers many chances for discovery and growth.
As Russian changes with the times, its importance and value grow. By tackling its challenges and complexities, people can gain a new level of cultural insight. This makes Russian a true global treasure.
FAQ
How important and prevalent is the Russian language?
Russian is a key language spoken by 265 million people worldwide. It ranks as the 8th most spoken language globally. It’s one of the six official languages at the United Nations. Russian is official in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan. It also has regional status in Ukraine, Georgia, Romania, and Moldova.
It serves as the common language in Central Europe, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe in former Soviet states.
Where is Russian spoken?
Russian is the official language in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan. It’s also recognized regionally in Ukraine, Georgia, Romania, and Moldova. In former Soviet states, it’s the common language in Central Europe, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe.
What language family does Russian belong to?
Russian is a Slavic language within the Indo-European family. It’s closely related to Ukrainian and Belarusian. It also shares similarities with Polish, Slovak, and Czech. Russian is the most spoken and relevant Slavic language today.
How did the Russian language develop historically?
The Russian language’s roots trace back to Proto-Slavic. By 500 CE, it split into West-, South-, and East-Slavic branches. The Grand Duchy of Moscow laid the foundation for modern Russian.
Through two World Wars and the Cold War, Russia rose to global prominence. The USSR’s spread led to the Russian language’s global reach.
How did the Russian language change in the 20th century?
Education and administration made Russian widespread in former Soviet states. This made it a common language in many areas. The media boom in the latter half of the century helped standardize Russian, reducing dialect diversity.
Today, while dialects still exist, standard Russian dominates due to its widespread use.
What is the Russian alphabet and writing system like?
The Russian alphabet is Cyrillic, derived from Greek with Latin influences. It has 33 letters, many unlike their Latin counterparts. Learning the Cyrillic alphabet is relatively straightforward for most learners.
How are consonants pronounced in Russian?
Russian has 21 consonants, 15 of which have two pronunciations. Hard consonants are pronounced without palatalization, while soft ones are palatalized, like with a ‘y’ after them. The softness of a consonant depends on the following letter. Russian also has voiced and voiceless pairs of consonants.
What are the vowel sounds in Russian?
Russian has 6 basic vowel sounds represented by 10 letters. Paying attention to vowel stress is crucial, as it can change word meanings. Effective pronunciation of vowels is key to speaking Russian well.
What are some key challenges for English speakers learning Russian?
The Cyrillic alphabet can be tough for English speakers at first but gets easier with practice. Russian’s case system, where nouns and adjectives change form based on sentence function, can be challenging. However, Russian’s flexible word order helps balance out the complexity of cases.
Oualid Cheddadi is the founder of Lingualid, a platform that inspires independent language learners worldwide, regardless of the language they are learning. The name “Lingualid” is derived from the Portuguese word for “language,” “língua,” and the last three letters of Oualid’s name, “Lid.”