Morocco is a country where many different languages come together, reflecting its rich history and diverse culture. Morocco boasts a unique blend of languages that tell the story of its diverse heritage. From the classical elegance of Arabic to the indigenous resonance of Amazigh languages, and the colonial imprints of French and Spanish, Morocco’s multilingualism is a testament to its dynamic history and societal evolution. This article explores the fascinating languages of Morocco, shedding light on their origins, roles, and the intricate ways they shape the nation’s identity and everyday life.
Key Takeaways
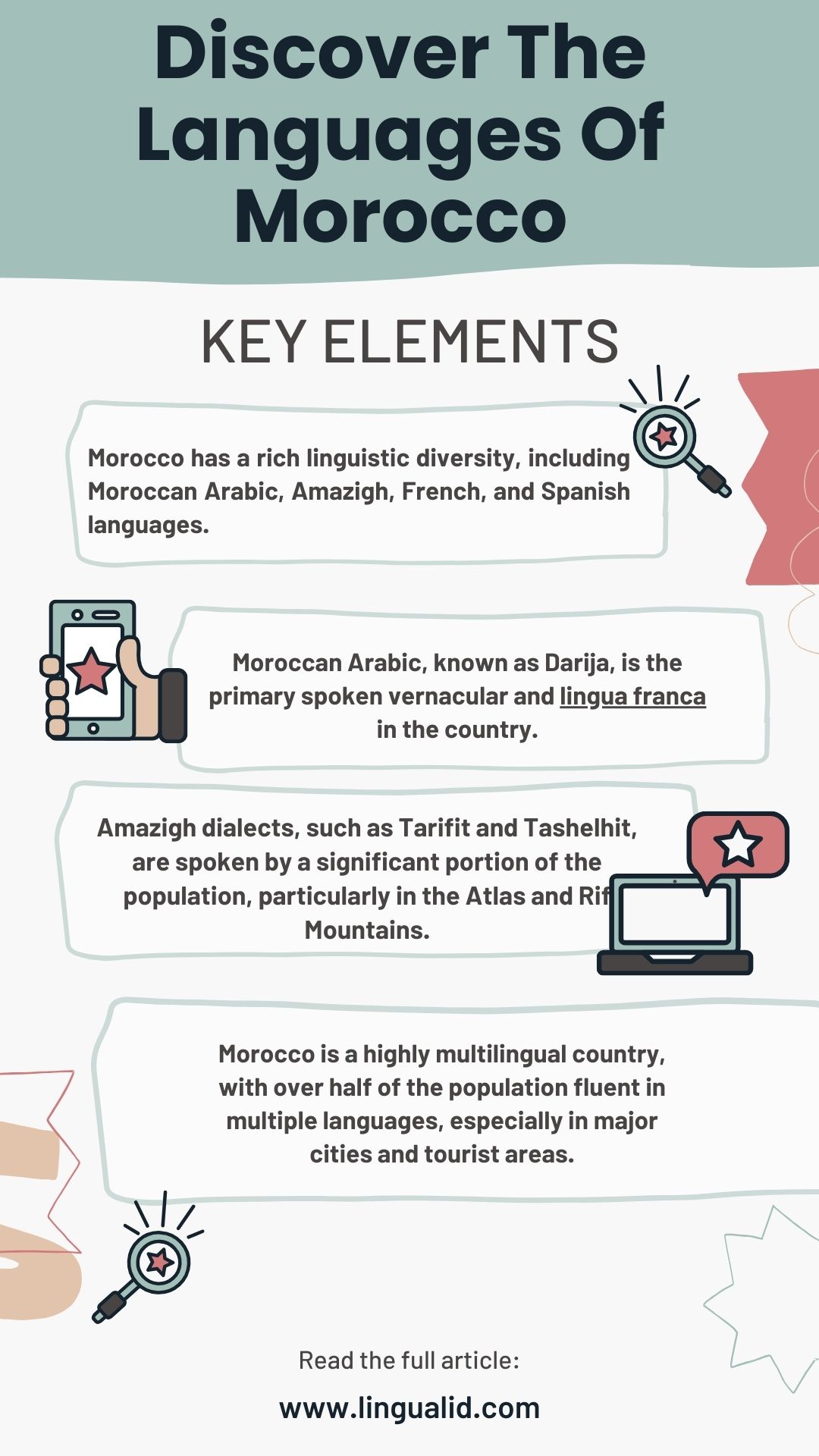
- Morocco has a rich linguistic diversity, including Moroccan Arabic, Amazigh, French, and Spanish languages.
- Moroccan Arabic, known as Darija, is the primary spoken vernacular and lingua franca in the country.
- Amazigh dialects, such as Tarifit and Tashelhit, are spoken by a significant portion of the population, particularly in the Atlas and Rif Mountains.
- French and Spanish have had a significant influence on Morocco due to its colonial history, with French being widely spoken and Spanish prevalent in the northern regions.
- Morocco is a highly multilingual country, with over half of the population fluent in multiple languages, especially in major cities and tourist areas.
- Key Takeaways
- Amazigh dialects (Tamazight)
- The Prevalence of French
- The Impact of Spanish
- Differences from Standard Arabic
- Regional Variations
- Tarifit and Tashelhit
- The Tamazight Language Family
- Historical Influences
- Multilingualism in Modern Morocco
- What are the main languages spoken in Morocco?
- What is the official language of Morocco?
- What is Moroccan Arabic (Darija)?
- What are the Amazigh languages of Morocco?
- What is the role of French and Spanish in Morocco?
- How has the use of English evolved in Morocco?
- What is the linguistic diversity of Morocco?
- How have language policies and education reforms in Morocco evolved?
The Official Languages of Morocco
Morocco is home to many languages, making it linguistically diverse. The main official languages are Modern Standard Arabic and Standard Moroccan Amazigh (also known as Tamazight).
Moroccan Arabic (Darija) is the most common language, spoken by about 91% of people. It is the everyday language and the common language for communication across the country. Darija has different ways of speaking, words, and grammar in different areas.
Amazigh dialects (Tamazight)
The Amazigh dialects, like Tarifit and Tashelhit, are popular in Morocco. Around 16 million Moroccans speak Amazigh. The Tamazight language family includes many local dialects, each with its own special traits.
“Amazigh was recognized as an official language in Morocco in 2011, marking a significant milestone in the recognition and preservation of the country’s linguistic diversity.”
Recognizing the Amazigh language as official is a big step. It helps protect the language and the rights of Moroccan Amazigh communities.
The Influence of Colonial Languages
Morocco has been shaped by two main colonial languages: French and Spanish. The French took over Morocco from 1907 until it gained independence in 1956. They made French a key language in schools, government, and media. Today, over 30% of Moroccans speak French.
Parts of Morocco were also under the Spanish protectorate. Spanish is common in the north, especially among those who have returned from Spain. This is because some Spanish territories share a border with Morocco.
The Prevalence of French
The French influence on Morocco’s language was big. During the French rule, French became an official language. It was used a lot in government, schools, and media. This made many people, especially in cities and those with more education, learn French.
The Impact of Spanish
The Spanish protectorate also changed Morocco’s language scene. In the north, Spanish is spoken a lot, mainly by those connected to the old Spanish areas. This shows the lasting effect of Spanish on Morocco and the ongoing links between the two countries.
| Language | Prevalence in Morocco |
|---|---|
| French | More than 30% of the population is fluent in French, due to its use during the French protectorate. |
| Spanish | Widely spoken in the northern regions, particularly among communities with ties to the former Spanish territories. |
The influence of French and Spanish from colonial times still affects Morocco’s language today. It has shaped the country’s mix of languages and the discussions on language policies and education.
The Uniqueness of Moroccan Arabic (Darija)
Moroccan Arabic, known as Darija, is a special dialect. It shares some parts of Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) but has its own unique sound, grammar, and ways of speaking. This makes Darija a key part of Morocco’s culture.
Differences from Standard Arabic
Darija is about 70% Arabic and also has influences from French, Spanish, and Amazigh languages. This mix leads to differences from MSA. For example, Darija is the fastest-speaking dialect in the Arab World. It changes over time, with new English words added, old ones disappearing, and education playing a role in how it’s spoken.
Regional Variations
- Moroccan Arabic has regional differences, with three main types across the country. These dialects often include words from European or indigenous languages of the area.
- Upper-class Moroccans often use more French in their Darija than those from lower classes. This shows the language’s variety in the country.
Knowing about Moroccan Arabic’s uniqueness is important. It helps people understand all Arabic dialects, making communication across the Arab world better. Learning Darija can improve cultural understanding, earn respect, and help in business dealings in Morocco.
Languages of Morocco
Morocco is home to many languages, making it linguistically diverse. Modern Standard Arabic and Amazigh are official languages. Moroccan Arabic (Darija) is the main language people use every day. French, Spanish, and English also play big roles in the country.
Moroccan Arabic, or Darija, is spoken by 98% of Moroccans. It’s used in TV, movies, and ads. This dialect is different from Modern Standard Arabic, showing Morocco’s unique language identity.
French is important too, used by 63% of people for official tasks. English is spoken by 14% and is getting more popular, especially in big cities and with international contacts.
Moroccans speak Amazigh dialects like Tarifit, Tashelhit, and Central Atlas Tamazight. These languages are mainly spoken in the Rif, Middle Atlas, and High Atlas mountains. They have a long history in Morocco and are now official languages.
Spanish is spoken by 10% of Moroccans, mostly in the north. This is because of Spain’s influence in areas like Tetouan, Chefchaouen, Tangier, and Nador.
Morocco’s language diversity shows its rich culture and history. Many languages, from official to everyday ones, highlight Moroccan society’s multilingual nature. This diversity is celebrated and preserved in the country.
The Amazigh Dialects of Morocco
Morocco is home to a rich mix of languages, thanks to the Amazigh dialects, also known as Tamazight. These ancient tongues are spoken by a big part of the population. They have survived through many years of cultural exchange and influence.
Tarifit and Tashelhit
In Morocco, two Amazigh dialects are especially important: Tarifit in the north and Tashelhit in the center. Tarifit is spoken by people in the Rif Mountains. Tashelhit is spoken by people in the High Atlas, Anti-Atlas, and Sous Valley regions of southwest Morocco.
The Tamazight Language Family
Amazigh language, known as Tamazight, belongs to the Afro-Asiatic language group. They are spoken by 60-80% of Moroccans, often alongside Arabic. The Tamazight family includes dialects like Kabyle, Central Atlas Tamazight, and Shawiya, each with its own unique traits and regional differences.
| Amazigh Dialect | Region |
|---|---|
| Tashelhiyt | High Atlas, Anti-Atlas, Sous Valley |
| Central Atlas Tamazight | Middle Atlas Mountains |
| Tarifit | Rif Mountains |
The Amazigh dialects have their own sound systems, structures, and words. These have been shaped by centuries of contact with Arabic. Despite the challenges, the Moroccan government is working to protect these languages. This includes setting up the Royal Institute for Amazigh Culture in 2001.
The Role of English in Morocco
In recent decades, the English language has become more important in Morocco. This is especially true in education and business. After changes in education in the early 2000s, English use grew. It’s now seen as key for doing business worldwide and a valuable skill for Moroccans.
A 2021 survey by the British Council found interesting facts. 40% of young Moroccans think English is the most important language to learn. Only 10% picked French. This shows a shift towards English among Moroccan youth.
The Moroccan government is boosting English language education. In May 2023, the Ministry of Education said English language instruction will start in middle school by 2025. This move aims to prepare Moroccan students for the global stage.
English is also making its mark outside of schools. There’s a rise in trilingual private schools and English programs in universities. This meets the growing need for English language skills.
Why do Moroccan youth prefer English? It’s because it’s the top language online and key in business and science worldwide. Plus, English-speaking countries have a big impact through media, making English more appealing to students.
Choosing English is not just practical. It’s also seen as a neutral language, free from the colonial past tied to French. This helps bridge social class gaps.
| Metric | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Young Moroccans who consider English the most important language to learn | 40% |
| Young Moroccans who consider French the most important language to learn | 10% |
The growing role of English in Morocco shows the country’s readiness for the global stage. It’s all about getting citizens ready for the 21st century’s challenges and chances.
The Linguistic Tapestry of Morocco
Morocco’s language mix shows its deep history and cultural blend. Over time, Phoenician, Punic, and Amazigh dialects were spoken here. Arabic came in the 8th century with the Muslim arrival. It slowly spread, but Amazigh languages stayed common in the countryside.
The influence of France and Spain during colonial times also shaped Morocco’s languages. Now, Morocco is a multilingual society. Many people speak Moroccan Arabic, Amazigh, French, and Spanish, based on where they live and their background.
Historical Influences
The history of Morocco’s languages is complex. The Amazigh people have spoken Tamazight, Tashelhit, and Tarifit for a long time. These languages are tied to certain areas and groups. Arabic came later and blended with the local languages, making Moroccan Arabic (Darija) a common language today.
Multilingualism in Modern Morocco
Today, Morocco’s language mix is still rich. French is big among the city folks and the well-educated, with 30% speaking it well. Spanish is popular in the north, showing Morocco’s past with Spain. English is getting more popular, especially with the young, for talking to people around the world.
Morocco’s language scene is lively and ever-changing. It shows the country’s cultural depth and its ability to adapt. From old Amazigh tongues to colonial languages, Morocco’s language mix keeps growing. It mirrors the country’s rich and complex identity.
Language Policies and Education Reforms
Morocco’s language scene has a rich history of policies and reforms. After becoming independent in 1956, it started a push to make Arabic the main language, replacing French. But, French still holds a big place, especially in schools and government.
In the early 2000s, Morocco saw the value in speaking many languages and made changes to education. These changes included teaching Amazigh languages and recognizing their importance. The country also saw the growing need for English in society.
The Education Bill of 2019 caused a lot of debate. The Justice and Development Party had different views on it. The bill requires teaching French and English in high school, but it also raised questions about Arabic and Amazigh languages in schools.
Morocco’s language policies are closely linked to its politics and culture. Making Tamazight an official language in 2011 was a big step for the Amazigh people. Yet, there are still challenges, like many students in poor or rural areas not speaking foreign languages well.
As Morocco deals with these language and education changes, it must balance keeping its culture with the need for global skills. Knowing many languages is key for getting ahead in school and work today.
Conclusion
Morocco’s language scene shows its deep cultural roots and the mix of influences it has seen. Moroccan Arabic (Darija) and Amazigh are common, along with French and Spanish from colonial times. This mix shows a blend of local and global cultures.
The country’s language policies aim to keep national languages alive while embracing diversity. They also meet the needs of a modern, connected world. This balance is key to Morocco’s language scene.
Throughout history, Morocco has valued its language diversity. This shows how resilient and flexible its people are. As Morocco changes, its languages will keep playing a big role in its culture. They make the Moroccan experience richer for locals and visitors.
Morocco’s language diversity reflects its complex history and its effort to keep culture alive in a changing world. By working to protect its languages, Morocco keeps its unique culture proud. This shows the strong spirit of its people.
FAQ
What are the main languages spoken in Morocco?
In Morocco, you’ll find Moroccan Arabic (Darija), Amazigh languages, French, and Spanish as the main languages.
What is the official language of Morocco?
Morocco’s official languages are Modern Standard Arabic and Standard Moroccan Amazigh.
What is Moroccan Arabic (Darija)?
Moroccan Arabic, or Darija, is the most common language in Morocco. It’s a unique dialect that blends some Modern Standard Arabic with its own special way of speaking, including different sounds, grammar, and phrases.
What are the Amazigh languages of Morocco?
The Amazigh languages in Morocco include Tarifit in the north and Tashelhit in the center. They belong to the Tamazight language family. This family is spoken by about 60-80% of Moroccans.
What is the role of French and Spanish in Morocco?
French and Spanish have a big impact on Morocco because of its history with these countries. Over 30% of Moroccans speak French as a second language. Spanish is also common, especially in the north, among people who have returned from Spain.
How has the use of English evolved in Morocco?
English has become more popular in Morocco over the years, especially in schools and business. This change started with education reforms in the early 2000s. Now, English is seen as a key language for doing business worldwide.
What is the linguistic diversity of Morocco?
Morocco is known for its diverse languages, including Moroccan Arabic, Amazigh languages, French, Spanish, and English. This mix shows the country’s rich history and cultural mix.
How have language policies and education reforms in Morocco evolved?
After gaining independence in 1956, Morocco tried to make Arabic the main language, replacing French. But French didn’t disappear. In the early 2000s, the country recognized the value of speaking many languages. They changed education to include Amazigh languages and promote speaking them.
Oualid Cheddadi is the founder of Lingualid, a platform that inspires independent language learners worldwide, regardless of the language they are learning. The name “Lingualid” is derived from the Portuguese word for “language,” “língua,” and the last three letters of Oualid’s name, “Lid.”