Korean is a fascinating language that has caught the eye of people all over the world. It is spoken by over 75 million people. It is the official language of both North and South Korea. It also has a big following in China, the United States, and Japan.
This ancient language has a long history, dating back to the Stone Age. It has grown and changed over time. The 15th century saw the creation of its unique writing system, Hangul.
As we explore the Korean language, we’ll learn about its origins and global reach. We’ll also see its cultural importance. This guide will help you understand the Korean language’s history, its family, and its unique features. You’ll also discover the differences between North and South Korean dialects.

- Key Takeaways
- Origins and Development
- Global Language Statistics
- Cultural Significance
- Altaic Language Connection
- Relationship with Other Asian Languages
- Linguistic Features
- Creation and Design
- Writing Rules and Patterns
- Basic Grammar Rules
- Honorific System
- Verb Conjugation
- Chinese Influence
- Modern Loanwords
- Native Korean Terms
- Online Learning Platforms
- Traditional Learning Methods
- Language Proficiency Tests
- How many people speak the Korean language worldwide?
- What is the history and origin of the Korean language?
- How is the Korean language related to other Asian languages?
- What are the key features of the Korean language?
- What is the Hangul writing system, and how does it work?
- How do the North and South Korean dialects differ?
- What is the role of the Korean language in modern Korean culture?
- What resources are available for learning the Korean language?
Key Takeaways
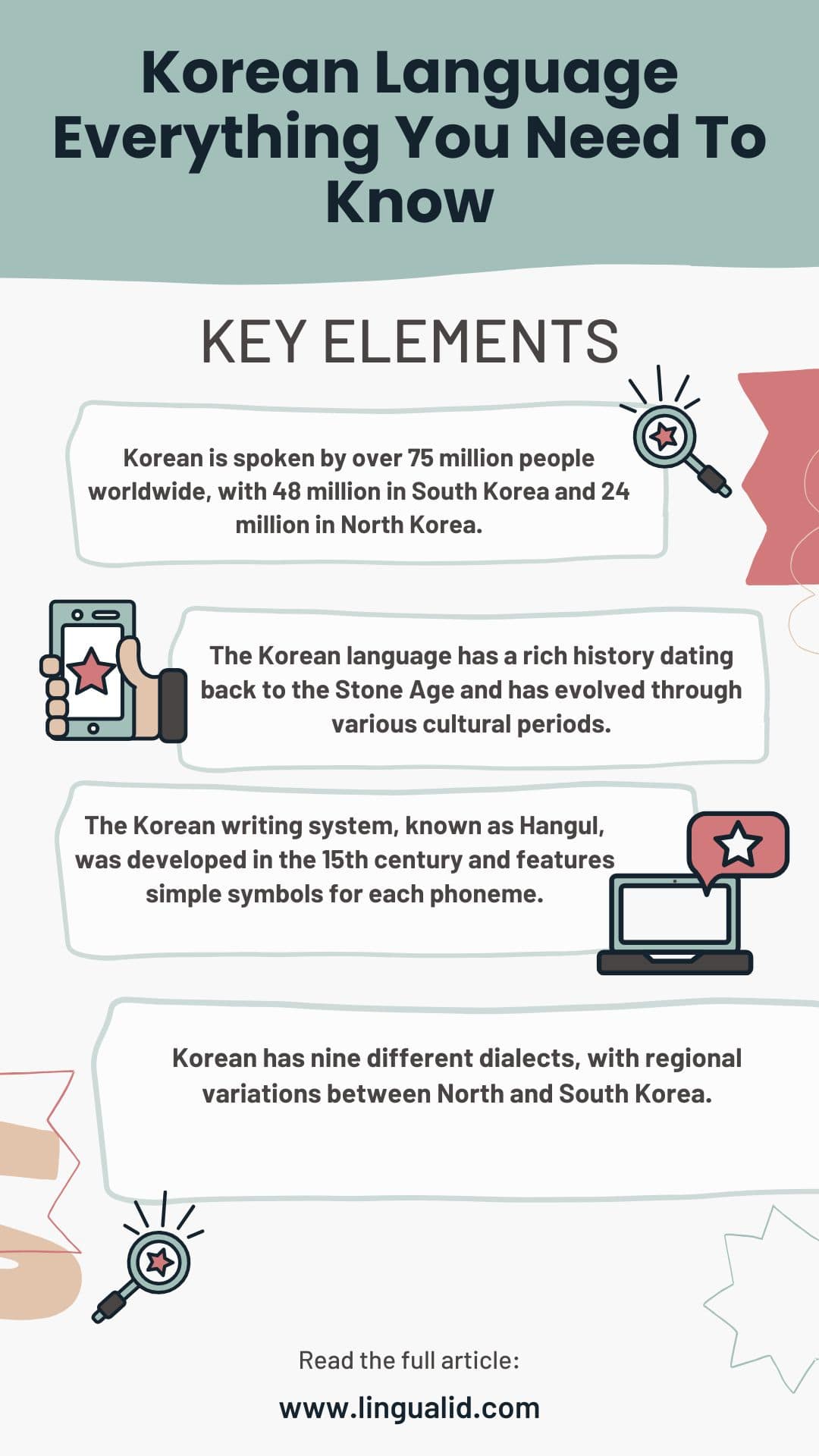
- Korean is spoken by over 75 million people worldwide, with 48 million in South Korea and 24 million in North Korea.
- The Korean language has a rich history dating back to the Stone Age and has evolved through various cultural periods.
- Korean is the official language of both North and South Korea, and is also an official language in the Yanbian region of China.
- The Korean writing system, known as Hangul, was developed in the 15th century and features simple symbols for each phoneme.
- Korean has nine different dialects, with regional variations between North and South Korea.
Introduction to the Korean Language World
The Korean language has a rich history. It started with different groups in the Korean peninsula. By the 6th to 14th centuries, they united into one language. Today, over 75 million people speak it worldwide.
It’s mainly spoken in South Korea, North Korea, China, the United States, and Japan. The language is key to Korean traditions, Korean lifestyle, and Korean society. It shows the culture’s values through its honorific system. It also helps keep important customs alive.
Origins and Development
The Korean language has been around since 57 BC. It has changed over time, influenced by many sources. The writing system, Hangul, was created in 1445 by King Sejong the Great. It made learning to read easier.
Hangul has 24 letters, with 14 consonants and 10 vowels. It’s organized into syllabic blocks. This makes it simpler to learn than other Asian writing systems.
Global Language Statistics
Korean is the 13th most spoken language globally. It’s the 8th most spoken in the United States, second among Asian languages. Its popularity is growing.
Korean traditions, Korean lifestyle, and Korean society are becoming more known worldwide.
Cultural Significance
The Korean language is deeply connected to the country’s culture. It helps keep Korean traditions and customs alive. The honorific system shows the importance of respect and social status.
The language is also central to Korean lifestyle and daily life. Korean is the main way people communicate. It’s a source of pride for its speakers.
The History and Evolution of Korean
The Korean language has a long and interesting history. It goes back to the Stone Age. Over time, it has changed a lot, leaving a lasting impact on its growth.
The first Korean writing was around 3 BCE. The first written records were in the 10th century as hyangga poems. Then, in the 15th century, it entered the Middle Korean era. This was when the famous Hangul writing system was created by King Sejong the Great.
Hangul was a new script made to show the sounds of Korean better. At first, the aristocracy didn’t like it because they used Hanja (Chinese characters). But, Hangul became more popular and is now a key part of Korean identity.
| Key Milestones in Korean Language History | Timeline |
|---|---|
| Earliest forms of Korean language | Around 3 BCE |
| First written records (hyangga poems) | 10th century |
| Middle Korean era | 15th century |
| Creation of Hangul writing system by King Sejong the Great | 15th century |
| Japanese colonial rule over Korea | 1910-1945 |
| Korea’s liberation from Japanese rule | 1945 |
| Emergence of modern Korean language | Post-1945 |
The Korean language has kept changing and growing. It has faced challenges like foreign rule and political changes. Now, it’s a lively and well-known language worldwide. It has over 81 million native speakers and is popular thanks to K-pop, Korean cinema, and technological advancements.
The Korean language has a fascinating history. It has been shaped by cultural exchange and language changes. From ancient times to today, it shows the strength and flexibility of the Korean people. It gives us a glimpse into their rich culture and a bright future.
Understanding Korean Language Family and Structure
The Korean language is part of its own family called Koreanic. It has interesting connections with other Asian languages. Knowing about the korean language structure and its ties to other languages helps us appreciate it more.
Altaic Language Connection
Some researchers think Korean might be related to Altaic languages. This group includes Turkic, Mongolian, and Tungus languages. They believe there could be historical and grammatical links, but the details are still debated.
Relationship with Other Asian Languages
Korean and Japanese share similarities in korean pronunciation and sentence order. Both use a subject-object-verb (SOV) pattern and particles for grammar. Korean also borrowed many words from Chinese, showing its influence.
Linguistic Features
- Korean is an agglutinative language, where words grow by adding parts to a base.
- It has a complex honorific system, showing respect and social rank through verb forms and words.
- Korean has a wide range of sounds, with 10 vowel and 21 consonant phonemes.
Looking into Korean’s unique traits and connections helps us understand its history and role in Asia’s languages.
Everything About Korean Language Today
The Korean language has a rich history, evolving over centuries. It has become the unique language we see today. Modern Korean uses the Hangul writing system and a complex honorific system. This shows the culture’s respect for hierarchy and social status.
The language has been influenced by English and other foreign languages, especially in South Korea. The National Institute of Korean Language supports this diversity. It does research and makes language policies to keep Korean alive.
Knowing Korean is key for work or visa needs in Korea. The Test of Proficiency in Korean (TOPIK) tests language skills. It has levels from beginner to advanced.
| Key Facts About the Korean Language | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Native Korean Speakers Worldwide | Approximately 80 million, with the majority residing in South Korea (50 million) and North Korea (25 million) |
| Composition of Korean Vocabulary | 60% Sino-Korean (derived from Chinese), 40% Native Korean and other foreign loanwords |
| Korean Language Dialects | 9 major regional dialects, with distinct variations between North and South Korea |
| Korean Language Proficiency Test | Test of Proficiency in Korean (TOPIK), widely used for work and visa purposes in Korea |
The Korean language has changed over time, adapting to cultural and political shifts. Today, it’s a vital part of the cultural identity for millions worldwide. They want to learn Korean and learn about the Korean language.
“The Korean language is a true testament to the resilience and unity of the Korean people, transcending borders and uniting a diverse global community.”
The Hangul Writing System
Korean language fans and scholars love the Korean alphabet, called Hangul. King Sejong the Great created it in 1443. It has 24 basic letters – 14 consonants and 10 vowels. These letters can be mixed to make over 11,000 characters.
Creation and Design
Hangul was made to help everyone read Korean. The letters were designed to show how sounds are made in the mouth. This makes reading Hangul easy and different from other Asian scripts.
Writing Rules and Patterns
Today, Korean writing has clear rules and patterns. Words are separated by spaces, and Western punctuation is used. Hangul’s design and simplicity have made it famous worldwide.
Related: Top Reasons To Learn Korean
Korean Language Dialects and Regional Variations
The Korean language is rich and diverse, with nine dialects across the Korean peninsula. The Seoul dialect is the standard in South Korea. Meanwhile, North Korea uses a mix of Seoul and Pyongyang dialects. Despite these differences, people can easily understand each other.
Regional accents and unique words are common. North Korean dialects are more distinct than those in South Korea. For example, the Gyeongsang dialect in the southeast has its own intonation and vocabulary. The Jeolla dialect in the southwest is known for its unique sound and rhythm.
| Dialect | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Seoul & Gyeonggi | The standard Korean dialect, used in media and education |
| Gangwon | Notable for pronunciation shifts and use of older Korean terms |
| Chungcheong | Known for its slower tempo and vowel shifts during verb conjugation |
| Gyeongsang | Characterized by a strong, brisk quality and pitch accent variations |
| Jeolla | Featuring distinctive intonation patterns, vowel harmony, and a melodic sound |
| Jeju | Considered a separate language, with nine Middle Korean vowels and additional consonants |
The variety of korean dialects and korean accent across the peninsula shows the language’s cultural depth. Despite the rise of standard Korean, keeping these dialects alive is vital. It helps preserve Korea’s linguistic and cultural diversity.

Korean Grammar and Sentence Structure
The Korean language has its own set of grammar rules and sentence structure. It’s both fascinating and challenging for learners. Korean sentences follow a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) order, unlike English’s Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) order. This means the subject comes first, followed by the object, and then the verb.
Basic Grammar Rules
Korean grammar includes particles, honorifics, and verb conjugations. These elements help form the sentence’s structure and meaning. Particles show the role of nouns in a sentence. The honorific system reflects the speaker’s relationship with the subject and audience through verb endings and other forms.
Honorific System
Verb conjugation is key in Korean grammar. Verbs change to show tense, aspect, mood, and honorifics. Learning these changes is vital for creating various sentences and conveying meaning.
Verb Conjugation
Grasping Korean grammar and sentence structure is essential for communication. Knowing the basic rules, honorific system, and verb conjugation helps learners express themselves clearly in Korean.
| Korean Sentence Structure | English Sentence Structure |
|---|---|
| Subject – Object – Verb (SOV) | Subject – Verb – Object (SVO) |
| 나는 학생이다. (I am a student.) | I am a student. |
| 저는 책을 읽습니다. (I read a book.) | I read a book. |
| 학교에 가요. (I go to school.) | I go to school. |
“Understanding the unique grammar and sentence structure of the Korean language is crucial for effectively communicating in this beautiful and expressive language.”
North and South Korean Language Differences
The Korean language is understood by both North and South Korea. Yet, they have developed their own unique differences. These differences are seen in vocabulary, pronunciation, and writing.
North Korea prefers native Korean language words. South Korea, on the other hand, uses more loanwords, especially from English. This choice reflects their different ideologies and cultures. North Korea’s Juche philosophy promotes pure Korean words. South Korea, being more open, welcomes global linguistic trends.
Pronunciation and accent also differ. The Pyongyang dialect in North Korea is different from Seoul’s dialect in the South. You can hear these differences in consonants, vowels, pitch, and rhythm.
The writing systems also show these differences. North Korea tries to remove Chinese characters (hanja) and foreign words from official use. South Korea still uses hanja in some cases. The way written Korean is formatted also varies between the two countries.
These differences highlight the unique cultural and sociopolitical identities of North and South Korea. Understanding these nuances is key for effective communication and collaboration between the two.
“The Korean language is not just a means of communication, but a reflection of the distinct histories and identities of North and South Korea.”
Korean Vocabulary and Word Origins
The Korean language is a rich tapestry of diverse vocabularies. It reflects Korea’s long and vibrant history. Native Korean words, known as 고유어 (goyu-eo), are at the heart of everyday language. But, the Korean lexicon has also been shaped by Chinese and English.
Chinese Influence
More than 50% of Korean vocabulary comes from Sino-Korean words. These are loanwords from Chinese, written with Chinese characters, or hanja. They are used in formal, academic, and technical areas. This shows the deep cultural and historical ties between Korea and China.
Modern Loanwords
The Korean language also has many loanwords from English. These words are common in technology, science, and popular culture. They show the global impact of Western culture. Examples include cup, pen, team, coffee, television, ice cream, shopping, hotel, date, and shirt.
Native Korean Terms
Despite Chinese and other languages’ influence, native 고유어 (goyu-eo) terms are at the core of Korean vocabulary. These words have been part of Korean for centuries. They cover everyday concepts, basic verbs, and fundamental language aspects. Learning about these native words gives insight into Korean culture.

Understanding the sources and influences on Korean vocabulary is crucial. It helps us appreciate the depth and complexity of this language. From Chinese characters to modern loanwords, the korean vocabulary reveals Korea’s rich cultural heritage and dynamic nature of the learn korean.
Korean Language in Modern Culture
The Korean language is now a big part of modern Korean culture. It’s influenced by K-pop, K-dramas, and Korean movies. These have made people all over the world want to learn Korean. In the U.S., more students are taking Korean classes, up 78% from 2009 to 2016.
Korean is closely tied to Korean food, with many food terms known globally. The language’s politeness system shows in how Koreans talk to each other and the world. Young people in Korea also use new slang and expressions, showing the language’s ability to change.
The Korean Wave, or Hallyu, has helped spread the Korean language. Korean entertainment and culture are loved by many, making people want to learn Korean. Duke University now offers more Korean classes, including ones on culture and history.
There are also cultural events like the Korean Program Party at Duke University. These events let students dive into the language and learn about Korean traditions. They show how much people value the Korean language and its role in modern Korean culture.
“Korean language courses at Duke University range from Elementary to Advanced levels, with additional courses focusing on Korean culture, literature, history, and society.”
The Korean language’s popularity is growing worldwide. It’s seen in K-pop, K-dramas, and Korean food. The language is a key part of Korea’s culture and heritage.
Learning Resources and Study Methods
Learning Korean is now easier than ever. There are many resources and methods to choose from. Whether you like online platforms, books, or programs, there’s something for everyone.
Online Learning Platforms
Apps like Duolingo and TTMIK (Talk To Me In Korean) make learning fun. They offer interactive lessons. Government sites also have great resources for learning Korean.
These platforms help you learn vocabulary, grammar, and speaking skills. You can do it all from home.
Traditional Learning Methods
- Textbooks: The KLEAR Integrated Korean and Korean Grammar in Use series are great for studying alone or in class.
- Language Exchange Programs: Join meetups or online forums to talk with native speakers.
- Immersion Courses: Take intensive programs to dive deep into the language and culture.
Language Proficiency Tests
The TOPIK (Test of Proficiency in Korean) is a key test for non-native speakers. It’s needed for school or work in Korea. Universities offer programs to help you pass the TOPIK and improve your Korean.
| Learning Resource | Key Features | Recommended for |
|---|---|---|
| Duolingo | Interactive, gamified lessons | Beginners and intermediate learners |
| TTMIK (Talk To Me In Korean) | Comprehensive lessons in various formats (podcasts, videos, textbooks) | Beginners to advanced learners |
| KLEAR Integrated Korean | Structured textbook series for self-study and classroom use | Beginners and intermediate learners |
| Korean Grammar in Use | In-depth grammar textbook for TOPIK preparation | Intermediate and advanced learners |
| TOPIK (Test of Proficiency in Korean) | Standardized proficiency test for non-native speakers | Learners seeking academic or professional opportunities in Korea |
With these many learning resources and study methods, you can start your Korean language journey. It opens doors to cultural exchange and new opportunities.
Conclusion
The Korean language is becoming more popular worldwide. It has a unique writing system and a rich cultural background. Learning Korean lets you explore both Korea’s past and its modern role in entertainment, technology, and food.
There are about 80 million people who speak Korean, and South Korea has a high literacy rate. The Hangul writing system and the way Korean sentences are structured make it both interesting and challenging. As Korean culture reaches more people, learning Korean is more appealing than ever.
If you want to learn about Korean history and culture, or if you need to communicate in Korean, this article is a great start. Dive into the Korean language’s complexity and discover a new world of culture and influence.
FAQ
How many people speak the Korean language worldwide?
What is the history and origin of the Korean language?
How is the Korean language related to other Asian languages?
What are the key features of the Korean language?
What is the Hangul writing system, and how does it work?
How do the North and South Korean dialects differ?
What is the role of the Korean language in modern Korean culture?
What resources are available for learning the Korean language?
Oualid Cheddadi is the founder of Lingualid, a platform that inspires independent language learners worldwide, regardless of the language they are learning. The name “Lingualid” is derived from the Portuguese word for “language,” “língua,” and the last three letters of Oualid’s name, “Lid.”